-40%
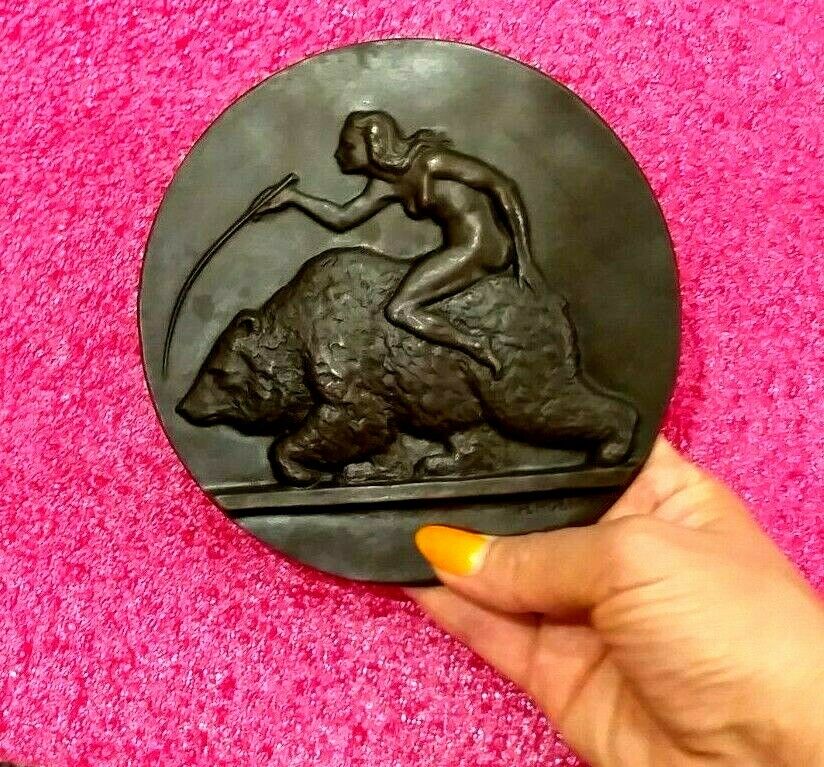
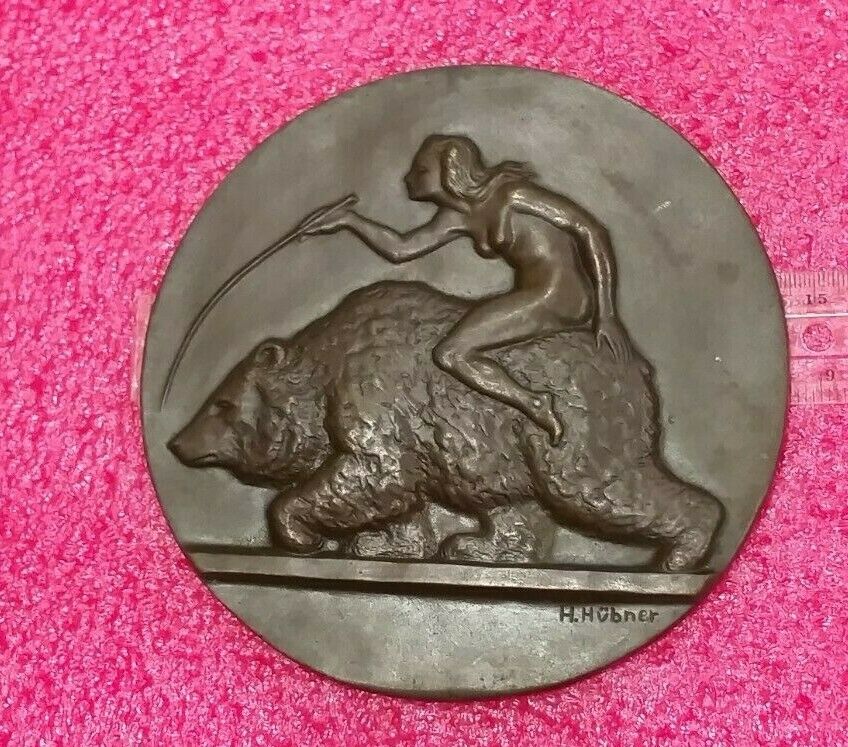
WW I 1914-1918 H.Hübner Nude German Lady Riding Russian Bear plaque medal 6"
$ 396
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Shipping from Europe with tracking number6 inches ,made in Germany /Austria
PATRIOTIC GERMAN /AUSTRIAN MEDAL IN MINT CONDITION !!! NOT USED !!!
ON MY AUCTION 99% MEDALS IN MINT OR EXTRA GOOD CONDITION !!!
World War I
Clockwise from the top:
The road to
Bapaume
in the aftermath of the
Battle of the Somme
, 1916
British
Mark V tanks
crossing the
Hindenburg Line
, 1918
HMS
Irresistible
sinking after hitting a
mine
in the
Dardanelles
, 1915
A British
Vickers machine gun
crew wears
gas masks
during the Battle of the Somme, 1916
German
Albatros D.III
biplane fighters near
Douai
, France, 1917
Date
28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918
(4 years, 3 months and 2 weeks)
Peace treaties
[show]
Location
Europe, Africa, the Middle East, the
Pacific Islands
, China, Indian Ocean, North and South Atlantic Ocean
Result
Allied
victory
Central Powers
victory on the
Eastern Front
nullified by defeat on the
Western Front
Fall of all continental empires in Europe (including
Germany
,
Russia
,
Ottoman Turkey
and
Austria-Hungary
)
Russian Revolution
and
Russian Civil War
, with the collapse of the
Russian Empire
and the subsequent formation of the
Soviet Union
Widespread unrest and
revolutions
throughout Europe and Asia
Creation of the
League of Nations
(
more
...
)
Territorial
changes
Formation of new countries in Europe and the Middle East
Transfer of
German colonies
and territories,
Partitioning the former Ottoman Empire
,
Austria-Hungary
and the
Russian Empire
, transfer of territories to other countries
Belligerents
Allied Powers
:
France
British Empire
[show]
Russia
[a]
(1914–17)
Serbia
Montenegro
Belgium
Japan
Italy
(1915–18)
United States
(1917–18)
Romania
(1916–18)
Portugal
(1916–18)
Hejaz
(1916–18)
China
(1917–18)
Greece
(1917–18)
Siam
(1917–18)
...
and others
Central Powers
:
Germany
Austria-Hungary
Ottoman Empire
Bulgaria
(1915–18)
...
and co-belligerents
Commanders and leaders
Raymond Poincaré
Georges Clemenceau
Herbert H. Asquith
David Lloyd George
Nicholas II
†
Alexander Kerensky
Victor Emmanuel III
Vittorio Orlando
Woodrow Wilson
Yoshihito
Albert I
Peter I
Ferdinand I
and others
...
Wilhelm II
Franz Joseph I
†
Karl I
Mehmed V
†
Mehmed VI
Three Pashas
Ferdinand I
and others
...
Strength
Total: 42,950,000
[1]
12,000,000
8,842,000
[2]
[3]
8,660,000
[4]
5,615,000
4,744,000
800,000
707,000
658,000
380,000
250,000
80,000
50,000
Total: 25,248,000
[1]
13,250,000
7,800,000
2,998,000
1,200,000
68,208,000 (Total all)
Casualties and losses
Military dead
: 5,525,000
Military wounded
: 12,832,000
Total:
18,357,000 KIA, WIA and MIA
Civilian dead:
4,000,000
further details
...
Military deaths by country
[5]
[6]
1,811,000
1,398,000
1,115,000
651,000
250,000–335,000
275,000
117,000
59,000–88,000
26,000
7,000
3,000
<1,000
Military dead:
4,386,000
Military wounded:
8,388,000
Total:
12,774,000 KIA, WIA and MIA
Civilian dead:
3,700,000
further details
...
Military deaths by country
[5]
2,051,000
1,200,000
772,000
88,000
show
v
t
e
Theatres of
World War I
hide
Events leading to
World War I
Franco-Prussian War
1870–1871
Congress of Berlin
1878
Dual Alliance
1879
Triple Alliance
1882
Franco-Russian Alliance
1894
Anglo-German naval arms race
1898–1912
Entente Cordiale
1904
Russo-Japanese War
1904–1905
First Moroccan Crisis
1905–1906
Anglo-Russian Entente
1907
Bosnian Crisis
1908–1909
Agadir Crisis
1911
Italo-Turkish War
1911–1912
Balkan Wars
1912–1913
Assassination of Franz Ferdinand
1914
July Crisis
1914
v
t
e
World War I: Mobilized forces per total population (in %)
[
citation needed
]
World War I
(or the
First World War
, often abbreviated as
WWI
or
WW1
) was a
global war
that lasted from 28 July 1914 to 11 November 1918. Contemporaneously known as the
Great War
or "
the war to end all wars
",
[7]
it led to the mobilisation of more than 70 million
military personnel
, including 60 million Europeans, making it one of the largest wars in history.
[8]
[9]
It is also
one of the deadliest conflicts in history
,
[10]
with an estimated nine million combatant deaths and 13 million civilian
deaths as a direct result of the war
,
[11]
while
resulting genocides
and the related
1918 influenza pandemic
caused another 17–100 million deaths worldwide.
[12]
[13]
On 28 June 1914,
Gavrilo Princip
, a
Bosnian Serb
Yugoslav nationalist
,
assassinated
the Austro-Hungarian heir
Archduke Franz Ferdinand
in
Sarajevo
, leading to the
July Crisis
.
[14]
[15]
In response,
Austria-Hungary
issued an ultimatum to
Serbia
on 23 July. Serbia's reply failed to satisfy the Austrians, and the two moved to a war footing. A network of interlocking alliances enlarged the crisis from a bilateral issue in the
Balkans
to one involving most of Europe. By July 1914, the
great powers
of Europe were divided into two coalitions: the
Triple Entente
, consisting of
France
,
Russia
, and
Britain
; and the
Triple Alliance
of
Germany
, Austria-Hungary, and
Italy
. The Triple Alliance was only defensive in nature, allowing Italy to stay out of the war until
April 1915
, when it joined the
Allied Powers
after its relations with Austria-Hungary deteriorated.
[16]
Russia felt it necessary to back Serbia, and approved partial mobilisation after Austria-Hungary shelled the Serbian capital of
Belgrade
on 28
July.
[17]
Full Russian mobilisation was announced on the evening of 30
July; the following day, Austria-Hungary and Germany did the same, while Germany demanded Russia demobilise within twelve hours.
[18]
When Russia failed to comply, Germany declared war on Russia on 1
August in support of Austria-Hungary, the latter following suit on 6
August; France ordered full mobilisation in support of Russia on 2
August.
[19]
Germany's strategy for a war on two fronts against France and Russia was to rapidly concentrate the bulk of its army in the West to defeat France within six weeks, then shift forces to the East before Russia could fully mobilise; this was later known as the
Schlieffen Plan
.
[20]
On 2
August, Germany demanded
free passage through Belgium
, an essential element in achieving a quick victory over France.
[21]
When this was refused, German forces invaded Belgium on 3
August and declared war on France the same day; the Belgian government invoked the
1839 Treaty of London
and, in compliance with its obligations under this treaty, Britain declared war on Germany on 4
August. On 12 August, Britain and France also declared war on Austria-Hungary; on 23
August,
Japan
sided with Britain, seizing German possessions in
China
and the Pacific. In November 1914, the
Ottoman Empire
entered the war on the side of the Austria-Hungary and Germany, opening fronts in the
Caucasus
,
Mesopotamia
, and the
Sinai Peninsula
. The war was fought in (and drew upon) each power's colonial empire also, spreading the conflict to
Africa
and across the globe. The Entente and its allies eventually became known as the Allied Powers, while the grouping of Austria-Hungary, Germany and their allies became known as the
Central Powers
.
The German advance into France was halted at the
Battle of the Marne
and by the end of 1914, the
Western Front
settled into a
war of attrition
, marked by a long series of
trench lines
that changed little until 1917 (the
Eastern Front
, by contrast, was marked by much greater exchanges of territory). In 1915, Italy joined the Allied Powers and opened a
front in the Alps
.
Bulgaria
joined the Central Powers in 1915 and
Greece
joined the Allies in 1917, expanding the
war in the Balkans
. The United States initially remained neutral, though even while neutral it became an important supplier of war
materiel
to the Allies. Eventually, after the sinking of American merchant ships by German submarines, the declaration by Germany that its navy would resume unrestricted attacks on neutral shipping, and
the revelation
that Germany was trying to incite Mexico to initiate war against the United States, the
U.S. declared war on Germany
on 6
April 1917. Trained American forces did not begin arriving at the front in large numbers until mid-1918, but the
American Expeditionary Force
ultimately reached some two million troops.
[22]
Though
Serbia was defeated in 1915
, and
Romania
joined the Allied Powers in 1916
only to be defeated in 1917
, none of the great powers were knocked out of the war until 1918. The 1917
February Revolution
in Russia replaced the
Tsarist autocracy
with the
Provisional Government
, but continuing discontent with the cost of the war led to the
October Revolution
, the creation of the
Soviet Socialist Republic
, and the signing of the
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
by the new government in March 1918, ending Russia's involvement in the war. Germany now controlled much of eastern Europe and transferred large numbers of combat troops to the Western Front. Using
new tactics
, the
German March 1918 Offensive
was initially successful. The Allies fell back and held. The last of the German reserves were exhausted as 10,000 fresh American troops arrived every day. The Allies drove the Germans back in their
Hundred Days Offensive
, a continual series of attacks to which the Germans had no reply.
[23]
One by one the Central Powers quit. First Bulgaria, then the Ottoman Empire and the Austro-Hungarian empire. With its allies defeated,
revolution
at home, and the military no longer willing to fight,
Kaiser Wilhelm
abdicated on 9
November and Germany signed an
armistice on 11 November 1918
, ending the fighting.
World War I was a significant turning point in the political, cultural, economic, and social climate of the world. The war
and its immediate aftermath
sparked numerous
revolutions and uprisings
. The
Big Four
(Britain, France, the United States, and Italy) imposed their terms on the defeated powers in a series of treaties agreed at the 1919
Paris Peace Conference
, the most well known being the German peace treaty: the
Treaty of Versailles
.
[24]
Ultimately, as a result of the war, the Austro-Hungarian, German, Ottoman, and Russian Empires ceased to exist, and numerous new states were created from their remains. However, despite the conclusive Allied victory (and the creation of the
League of Nations
during the Peace Conference, intended to prevent future wars), a
second world war
followed just over
twenty years
later.