-40%
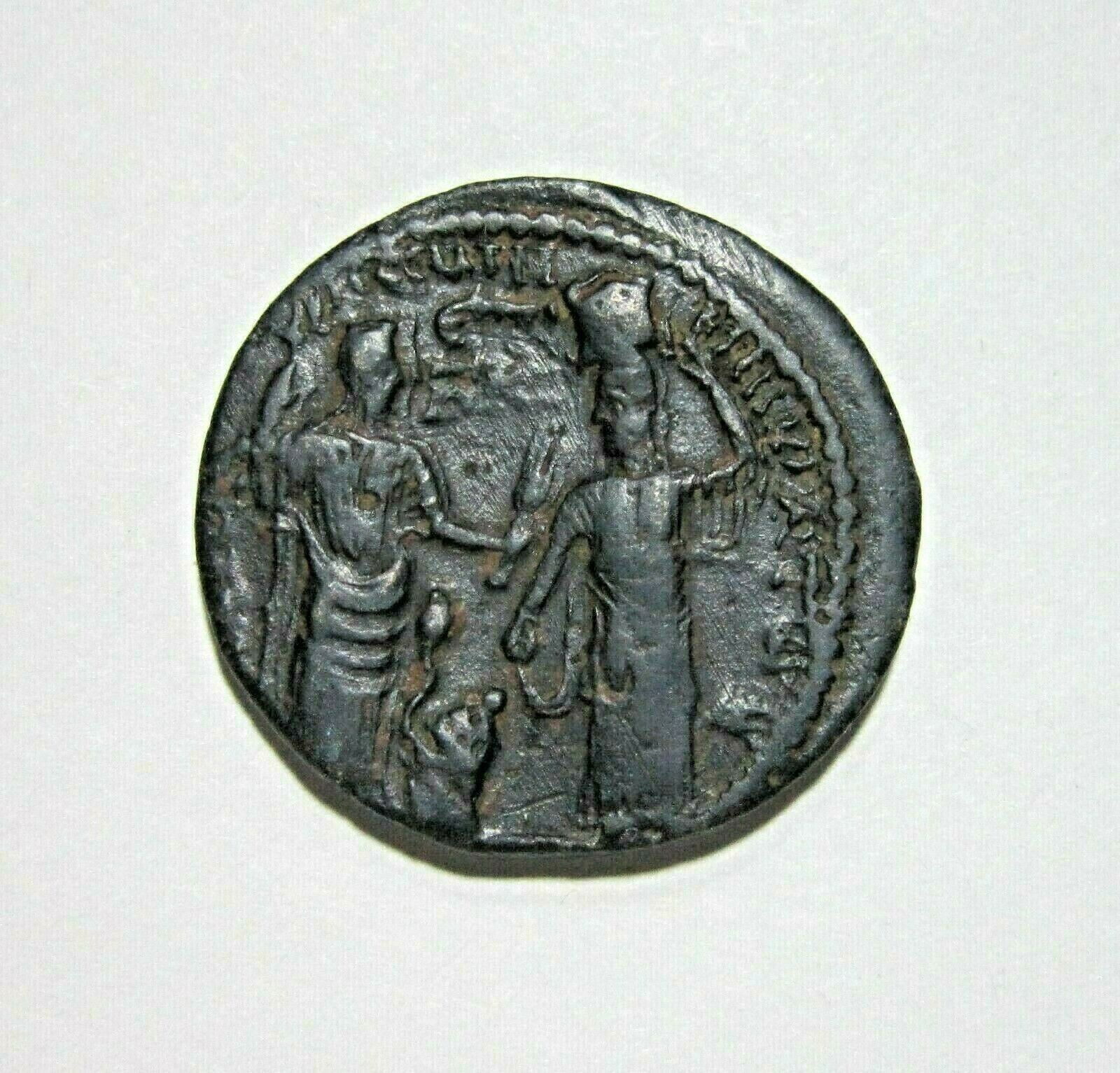
TRAJAN 109AD Perinthus Thrace LION SKIN CLUB of HERCULES Rare Roman Coin i58262
$ 200.64
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Item:i58262
Authentic Ancient Coin of:
Trajan - Roman Emperor : 98-117 A.D.
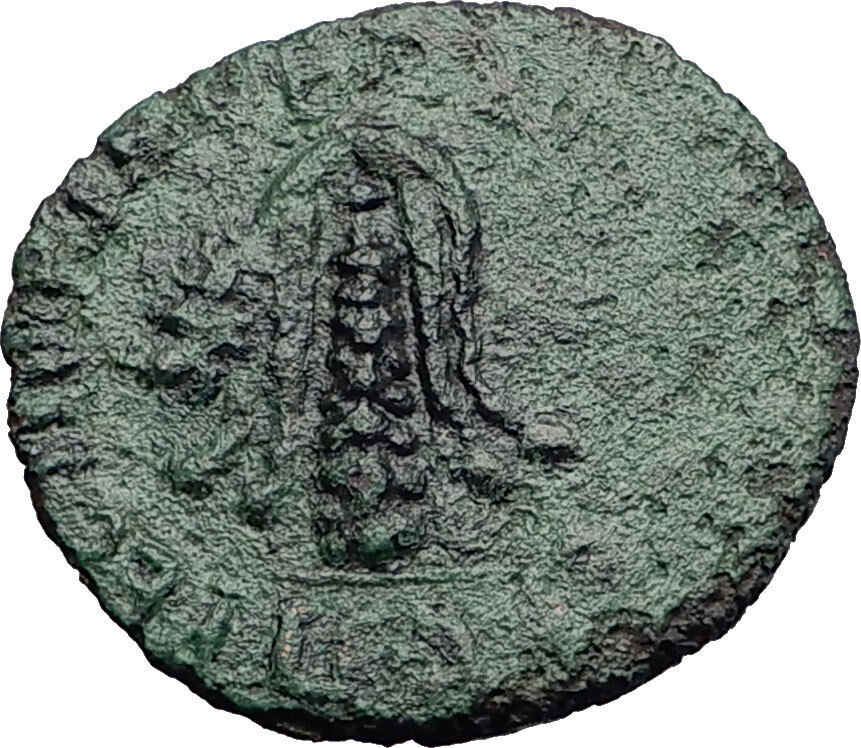
Bronze 21mm (5.08 grams) of Perinthus in Thrace, struck circa 109/112 A.D.
Iuventius Celsus, presbeutes
Reference: RPC III, 705; Sch 359-63
AYT NEP TPAIANOC KAI CE
ΓEP ΔA, laureate head of Trajan right with aegis on left shoulder.
EΠI IOYOY KEΛC ΠPEC ΠEPIN, lion skin over club of Hercules.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
Heracles
, born
Alcaeus
(
Alkaios
) or
Alcides
, was a
divine hero
in
Greek mythology
, the son of
Zeus
and
Alcmene
, foster son of
Amphitryon
and great-grandson and half-brother (as they are both sired by the god
Zeus
) of
Perseus
. He was the greatest of the Greek heroes, a paragon of masculinity, the ancestor of royal clans who claimed to be
Heracleidae
and a champion of the
Olympian order
against
chthonic
monsters. In
Rome
and the
modern
West
, he is known as
Hercules
, with whom the later
Roman emperors
, in particular
Commodus
and
Maximian
, often identified themselves. The Romans adopted the Greek version of his life and works essentially unchanged, but added anecdotal detail of their own, some of it linking the hero with the geography of the Central Mediterranean. Details of his
cult
were adapted to Rome as well.
Extraordinary strength,
courage
, ingenuity, and sexual prowess with both males and females were among the characteristics commonly attributed to him. Heracles used his wits on several occasions when his strength did not suffice, such as when laboring for the king
Augeas
of
Elis
, wrestling the giant
Antaeus
, or tricking
Atlas
into taking the sky back onto his shoulders. Together with
Hermes
he was the patron and protector of
gymnasia
and
palaestrae
. His iconographic attributes are the
lion skin
and the
club
. These qualities did not prevent him from being regarded as a playful figure who used games to relax from his labors and played a great deal with children. By conquering dangerous archaic forces he is said to have "made the world safe for mankind" and to be its benefactor. Heracles was an extremely passionate and emotional individual, capable of doing both great deeds for his friends (such as wrestling with
Thanatos
on behalf of Prince
Admetus
, who had regaled Heracles with his hospitality, or restoring his friend
Tyndareus
to the throne of
Sparta
after he was overthrown) and being a terrible enemy who would wreak horrible vengeance on those who crossed him, as Augeas,
Neleus
and
Laomedon
all found out to their cost.
Marmara Ereğlisi
, ancient Perinthos, later called Heracleia, Samian colony in the European coast of Propontis (today's Tekirdağ Province in the Marmara region of Turkey)
The town, originally a
Samian
colony, was founded as
Perinthos
(Πέρινθος), in English usually known by its Latinized form as
Perinthus
. In about 400 BC, it was given the name of
Heraclea
(Ἡράκλεια). It was built amphitheatre-like on the hillside of a cape extending into the
Sea of Marmara
, close to where the modern town stands. Its port and its happy situation at the junction of several great sea-routes, made it a town of commercial importance. It became famous because of its resistance to
Philip II of Macedon
. Many of its coins have come down to us, and give us information concerning the festivals held there.
Byzantine Emperor
Justinian I
restored its aqueducts and a palace.
At an early date, according to tradition in the
Apostolic Age
, Heraclea became a Christian
bishopric
. As capital of the
Roman province
of
Europa
, it was the
metropolitan see
for all the bishoprics of the province, including
Byzantium
, which in 330 became
Constantinople
. The see of Constantinople soon obtained superiority over Heraclea. However, Heraclea was recognized in the
Notitia Episcopatuum
of Pseudo-Epiphanius as having five
suffragan sees
:
Panium
,
Callipolis
,
Chersonesus in Europa
,
Coela
, and
Rhaedestus
. An early 10th-century
Notitia Episcopatuum
attributed to
Leo VI the Wise
lists the suffragans as 15 and another, dating from 1022-1025, puts them at 17. With the advance of the
Ottoman
conquests, the number of suffragans was severely reduced. In the early 20th century, it still had two suffragans. Today it is only a
titular
"Elder Metropolis and Exarchate of Thrace" of the
Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople
. In the 13th century, there were
Latin
diocesan bishops of Heraclea. Today, the
Catholic Church
lists it as a
titular see
.
Trajan - Roman Emperor : 98-117 A.D.
Caesar: 97 A.D. (under Nerva) | Augustus: 98-117 A.D.
| Adopted son of Nerva | Son of Trajan Pater | Husband of Plotina | Brother of Marciana | Uncle of Matidia | Grand-uncle of Sabina |
Marcus Ulpius Nerva Traianus
, commonly known as
Trajan
(18 September, 53 – 8 August, 117), was a
Roman Emperor
who reigned from AD 98 until his death in AD 117. Born
Marcus Ulpius Traianus
into a non-
patrician
family in the
Hispania Baetica
province (modern day
Spain
), Trajan rose to prominence during the reign of emperor
Domitian
, serving as a general in the
Roman army
along the
German frontier
, and successfully crushing the revolt of
Antonius Saturninus
in 89. On September 18, 96, Domitian was succeeded by
Marcus Cocceius Nerva
, an old and childless senator who proved to be unpopular with the army. After a brief and tumultuous year in power, a revolt by members of the
Praetorian Guard
compelled him to adopt the more popular Trajan as his heir and successor. Nerva died on January 27, 98, and was succeeded by his adopted son without incident.
As a civilian administrator, Trajan is best known for his extensive public building program, which reshaped the city of
Rome
and left multiple enduring landmarks such as
Trajan's Forum
,
Trajan's Market
and
Trajan's Column
. It was as a military commander however that Trajan celebrated his greatest
triumphs
. In 101, he launched a
punitive expedition
into the kingdom of
Dacia
against king
Decebalus
, defeating the Dacian army near
Tapae
in 102, and finally conquering Dacia completely in 106. In 107, Trajan pushed further east and annexed the
Nabataean kingdom
, establishing the province of
Arabia Petraea
. After a period of relative peace within the Empire, he launched his final campaign in 113 against
Parthia
, advancing as far as the city of
Susa
in 116, and expanding the Roman Empire to its greatest extent. During this campaign Trajan was struck by illness, and late in 117, while sailing back to Rome, he died of a
stroke
on
August 9
, in the city of
Selinus
. He was
deified
by the Senate and his ashes were laid to rest under
Trajan's Column
. He was succeeded by his adopted son (not having a biological heir)
Publius Aelius Hadrianus
—commonly known as Hadrian.
As an emperor, Trajan's reputation has endured - he is one of the few rulers whose reputation has survived the scrutiny of nineteen centuries of history. Every new emperor after him was honoured by the Senate with the prayer
felicior Augusto, melior Traiano
, meaning "may he be luckier than
Augustus
and better than Trajan". Among
medieval
Christian theologians, Trajan was considered a
virtuous pagan
, while the 18th century historian
Edward Gibbon
popularized the notion of the
Five Good Emperors
, of which Trajan was the second.
Early life and rise to power
Trajan was born on September 18, 53 in the Roman province of
Hispania Baetica
(in what is now
Andalusia
in modern Spain), a province that was thoroughly Romanized and called southern Hispania, in the city of
Italica
, where the
Italian
families were paramount. Of
Italian
stock himself, Trajan is frequently but misleadingly designated the first provincial emperor.
Trajan was the son of
Marcia
and
Marcus Ulpius Traianus
, a prominent
senator
and general from the famous
Ulpia
gens
. Trajan himself was just one of many well-known Ulpii in a line that continued long after his own death. His elder sister was
Ulpia Marciana
and his niece was
Salonina Matidia
. The
patria
of the Ulpii was
Italica
, in Spanish Baetica, where their ancestors had settled late in the third century B.C. This indicates that the Italian origin was paramount, yet it has recently been cogently argued that the family's ancestry was local, with Trajan senior actually a Traius who was adopted into the family of the Ulpii.
As a young man, he rose through the ranks of the
Roman army
, serving in some of the most contentious parts of the Empire's frontier. In 76–77, Trajan's father was
Governor
of
Syria
(
Legatus
pro praetore Syriae
), where Trajan himself remained as
Tribunus
legionis
. Trajan was nominated as
Consul
and brought
Apollodorus of Damascus
with him to
Rome
around 91. Along the
Rhine River
, he took part in the Emperor
Domitian
's wars while under Domitian's successor,
Nerva
, who was unpopular with the army and needed to do something to gain their support. He accomplished this by naming Trajan as his adoptive son and successor in the summer of 97. According to the
Augustan History
, it was the future Emperor
Hadrian
who brought word to Trajan of his adoption. When Nerva died on January 27, 98, the highly respected Trajan succeeded without incident.
His reign
The new Roman emperor was greeted by the people of Rome with great enthusiasm, which he justified by governing well and without the bloodiness that had marked Domitian's reign. He freed many people who had been unjustly imprisoned by Domitian and returned a great deal of private property that Domitian had confiscated; a process begun by Nerva before his death. His popularity was such that the
Roman Senate
eventually bestowed upon Trajan the
honorific
of
optimus
, meaning "the best".
Dio Cassius
, sometimes known as Dio, reveals that Trajan drank heartily and was
involved with boys
. "I know, of course, that he was devoted to boys and to wine, but if he had ever committed or endured any base or wicked deed as the result of this, he would have incurred censure; as it was, however, he drank all the wine he wanted, yet remained sober, and in his relation with boys he harmed no one." This sensibility was one that influenced his governing on at least one occasion, leading him to favour the king of Edessa out of appreciation for his handsome son: "On this occasion, however,
Abgarus
, induced partly by the persuasions of his son Arbandes, who was handsome and in the pride of youth and therefore in favour with Trajan, and partly by his fear of the latter's presence, he met him on the road, made his apologies and obtained pardon, for he had a powerful intercessor in the boy."
Dacian Wars
It was as a military commander that Trajan is best known to history, particularly for his conquests in the
Near East
, but initially for the two wars against
Dacia
— the reduction to client kingdom (101-102), followed by actual incorporation to the Empire of the trans-Danube border kingdom of Dacia—an area that had troubled Roman thought for over a decade with the unfavourable (and to some, shameful) peace negotiated by
Domitian
's ministers In the first war c. March–May 101, he launched a vicious attack into the kingdom of
Dacia
with four legions, crossing to the northern bank of the
Danube River
on a stone bridge he had built, and defeating the Dacian army near or in a
mountain pass
called
Tapae
(see
Second Battle of Tapae
). Trajan's troops were mauled in the encounter, however and he put off further campaigning for the year to heal troops, reinforce, and regroup.
Trajan's Column
.
During the following winter, King
Decebalus
launched a counter-attack across the
Danube
further downstream, but this was repulsed. Trajan's army advanced further into Dacian territory and forced King Decebalus to submit to him a year later, after Trajan took the Dacian capital/fortress of
Sarmizegethusa
. The Emperor Domitian had campaigned against
Dacia from 86 to 87
without securing a decisive outcome, and Decebalus had brazenly flouted the terms of the peace (89 AD) which had been agreed on conclusion of this campaign.
Trajan now returned to Rome in triumph and was granted the title
Dacicus Maximus
. The victory was celebrated by the
Tropaeum Traiani
. Decebalus though, after being left to his own devices, in 105 undertook an invasion against Roman territory by attempting to stir up some of the tribes north of the river against her.
Trajan took to the field again and after building with the design of
Apollodorus of Damascus
his
massive bridge over the Danube
, he conquered Dacia completely in 106. Sarmizegethusa was destroyed,
Decebalus
committed
suicide
, and his severed head was exhibited in Rome on the steps leading up to the
Capitol
. Trajan built a new city, "Colonia Ulpia Traiana Augusta Dacica Sarmizegetusa", on another site than the previous Dacian Capital, although bearing the same full name, Sarmizegetusa. He resettled Dacia with Romans and annexed it as a province of the Roman Empire. Trajan's Dacian campaigns benefited the Empire's finances through the acquisition of Dacia's gold mines. The victory is celebrated by
Trajan's Column
.
Expansion in the East
At about the same time
Rabbel II Soter
, one of Rome's client kings, died. This event might have prompted the annexation of the
Nabataean kingdom
, although the manner and the formal reasons for the annexation are unclear. Some epigraphic evidence suggests a military operation, with forces from
Syria
and
Egypt
. What is clear, however, is that by 107, Roman legions were stationed in the area around
Petra
and
Bostra
, as is shown by a papyrus found in Egypt. The empire gained what became the province of
Arabia Petraea
(modern southern
Jordan
and north west
Saudi Arabia
).
Period of peace
The next seven years, Trajan ruled as a civilian emperor, to the same acclaim as before. It was during this time that he corresponded with
Pliny the Younger
on the subject of how to deal with the
Christians
of
Pontus
, telling Pliny to leave them alone unless they were openly practicing the religion. He built several new buildings, monuments and roads in
Italia
and his native
Hispania
. His magnificent complex in Rome raised to commemorate his victories in
Dacia
(and largely financed from that campaign's loot)—consisting of a
forum
,
Trajan's Column
, and Trajan's Market still stands in Rome today. He was also
a prolific builder of triumphal arches
, many of which survive, and rebuilder of roads (
Via Traiana
and
Via Traiana Nova
).
One notable act of Trajan was the hosting of a three-month
gladiatorial
festival in the great
Colosseum
in Rome (the precise date of this festival is unknown). Combining chariot racing, beast fights and close-quarters gladiatorial bloodshed, this gory spectacle reputedly left 11,000 dead (mostly slaves and criminals, not to mention the thousands of ferocious beasts killed alongside them) and attracted a total of five million spectators over the course of the festival.
Another important act was his formalisation of the
Alimenta
, a welfare program that helped orphans and poor children throughout Italy. It provided general funds, as well as food and subsidized education. The program was supported initially by funds from the Dacian War, and then later by a combination of estate taxes and philanthropy.
[13]
. Although the system is well documented in literary sources and contemporary epigraphy, its precise aims are controversial and have generated considerable dispute between modern scholars: usually, it's assumed that the programme intended to bolster citzen numbers in Italy. However, the fact that it was subsidized by means of interest payments on loans made by landowners restricted it to a small percentage of potential welfare recipients (
Paul Veyne
has assumed that, in the city of
Veleia
, only one child out of ten was an actual beneficiary) - therefore, the idea, advanced by
Moses I. Finley
, that the whole scheme was at most a form of random charity, a mere imperial benevolence
[14]
.
Maximum extent of the Empire
The extent of the Roman Empire under Trajan (117)
In 113, he embarked on his last campaign, provoked by
Parthia
's decision to put an unacceptable king on the throne of
Armenia
, a kingdom over which the two great empires had shared
hegemony
since the time of
Nero
some fifty years earlier. Some modern historians also attribute Trajan's decision to wage war on Parthia to economic motives: to control, after the annexation of Arabia, Mesopotamia and the coast of the Persian Gulf, and with it the sole remaining receiving-end of the Indian trade outside Roman control - an attribution of motive other historians find absurd, as seeing a commercial motive in a campaign triggered by the lure of territorial annexation and prestige - by the way, the only motive for Trajan's actions ascribed by Dio Cassius in his description of the events. Other modern historians, however, think that Trajan's original aim was quite modest: to assure a more defensible Eastern frontier for the Roman Empire, crossing across Northern Mesopotamia along the course of the river
Khabur
in order to offer cover to a Roman Armenia.
Trajan marched first on Armenia, deposed the Parthian-appointed king (who was afterwards murdered while kept in the custody of Roman troops in an unclear incident) and annexed it to the Roman Empire as a province, receiving in passing the acknowledgement of Roman hegemony by various tribes in the Caucasus and on the Eastern coast of the Black Sea - a process that kept him busy until the end of 114
]
. The cronology of subsequent events is uncertain, but it's generally believed that early in 115 Trajan turned south into the core Parthian hegemony, taking the Northern Mesopotamian cities of
Nisibis
and
Batnae
and organizing a province of
Mesopotamia
in the beginning of 116, when coins were issued announcing that Armenia and Mesopotamia had been put under the authority of the Roman people.
In early 116, however, Trajan began to toy with the conquest of the whole of Mesopotamia, an overambitious goal that eventually backfired on the results of his entire campaign: One Roman division crossed the
Tigris
into
Adiabene
, sweeping South and capturing
Adenystrae
; a second followed the river South, capturing
Babylon
; while Trajan himself sailed down the
Euphrates
, then dragged his fleet overland into the Tigris, capturing
Seleucia
and finally the Parthian capital of
Ctesiphon
. He continued southward to the
Persian Gulf
, receiving the submission of Athambelus, the ruler of
Charax
, whence he declared Babylon a new province of the Empire, sent the Senate a laurelled letter declaring the war to be at a close and lamented that he was too old to follow in the steps of
Alexander the Great
and reach the distant
India
itself. A province of
Assyria
was also proclaimed, apparently covering the territory of Adiabene, as well as some measures seem to have been considered about the fiscal administration of the Indian trade.
However, as Trajan left the Persian Gulf for Babylon - where he intended to offer sacrifice to Alexander in the house where he had died in 323 B.C.- a sudden outburst of Parthian resistance, led by a nephew of the Parthian king, Sanatrukes, imperilled Roman positions in Mesopotamia and Armenia, something Trajan sought to deal with by forsaking direct Roman rule in Parthia proper, at least partially: later in 116, after defeating a Parthian army in a battle where Sanatrukes was killed and re-taking Seleucia, he formally deposed the Parthian king
Osroes I
and put his own puppet ruler
Parthamaspates
on the throne. That done, he retreated North in order to retain what he could of the new provinces of Armenia and Mesopotamia.
Bust of Trajan,
Glyptothek
,
Munich
.
It was at this point that Trajan's health started to fail him. The fortress city of
Hatra
, on the
Tigris
in his rear, continued to hold out against repeated Roman assaults. He was personally present at the
siege
and it is possible that he suffered a heat stroke while in the blazing heat. Shortly afterwards, the
Jews
inside the Eastern Roman Empire rose up in rebellion once more, as did the people of Mesopotamia. Trajan was forced to withdraw his army in order to put down the revolts. Trajan saw it as simply a temporary setback, but he was destined never to command an army in the field again, turning his Eastern armies over to the high ranking legate and governor of Judaea,
Lusius Quietus
, who in early 116 had been in charge of the Roman division who had recovered Nisibis and
Edessa
from the rebels; Quietus was promised for this a consulate in the following year - when he was actually put to death by
Hadrian
, who had no use for a man so committed to Trajan's aggressive policies.
Early in 117, Trajan grew ill and set out to sail back to Italy. His health declined throughout the spring and summer of 117, something publicy acknowledged by the fact that a bronze bust displayed at the time in the public baths of
Ancyra
showed him clearly aged and edemaciated. By the time he had reached Selinus in
Cilicia
which was afterwards called Trajanopolis, he suddenly died from
edema
on August 9. Some say that he had adopted
Hadrian
as his successor, but others that it was his wife
Pompeia Plotina
who hired someone to impersonate him after he had died.
Hadrian
, upon becoming ruler, recognized the abandonment of Mesopotamia and restored Armenia - as well as
Osroene
- to the Parthian hegemony under Roman suzerainty - a telling sign the Roman Empire lacked the means for pursuing Trajan's overambitious goals. However, all the other territories conquered by Trajan were retained. Trajan's ashes were laid to rest underneath Trajan's column, the monument commemorating his success.
The
Alcántara Bridge
, widely hailed as a masterpiece of
Roman engineering
.
Building activities
Trajan was a prolific builder in Rome and the provinces, and many of his buildings were erected by the gifted architect
Apollodorus of Damascus
. Notable structures include
Trajan's Column
,
Trajan's Forum
,
Trajan's Bridge
,
Alcántara Bridge
, and possibly the
Alconétar Bridge
. In order to build his forum and the adjacent brick market that also held his name Trajan had vast areas of the surrounding hillsides leveled.
Trajan's legacy
Unlike many lauded rulers in history, Trajan's reputation has survived undiminished for nearly nineteen centuries.
Ancient sources on Trajan's personality and accomplishments are unanimously positive. Pliny the younger, for example, celebrates Trajan in his panegyric as a wise and just emperor and a moral man.
Dio Cassius
admits Trajan had vices like heavy drinking and sexual involvement with boys, but added that he always remained dignified and fair. The
Christianisation
of Rome resulted in further embellishment of his legend: it was commonly said in
medieval
times that
Pope Gregory I
, through divine intercession, resurrected Trajan from the dead and baptized him into the Christian faith. An account of this features in the
Golden Legend
.
Theologians, such as
Thomas Aquinas
, discussed Trajan as an example of a virtuous pagan. In
the Divine Comedy
,
Dante
, following this legend, sees the spirit of Trajan in the Heaven of
Jupiter
with other historical and mythological persons noted for their justice.
He also features in
Piers Plowman
. An episode, referred to as the
justice of Trajan
was reflected in several art works.
In the 18th Century King
Charles III of Spain
comminsioned
Anton Raphael Mengs
to paint
The Triumph of Trajan
on the ceiling of the banqueting-hall of the
Royal Palace of Madrid
- considered among the best work of this artist.
"Traian" is used as a male first name in present-day
Romania
- among others, that of the country's incumbent president,
Traian Băsescu
.
Frequently Asked Questions
Mr. Ilya Zlobin, world-renowned expert numismatist, enthusiast, author and dealer in authentic ancient Greek, ancient Roman, ancient Byzantine, world coins & more.
Who am I dealing with?
You are dealing with Ilya Zlobin, ancient coin expert, enthusiast, author and dealer with an online store having a selection of over 15,000 items with great positive feedback from verified buyers and over 10 years experience dealing with over 57,000 ancient and world coins and artifacts. Ilya Zlobin is an independent individual who has a passion for coin collecting, research and understanding the importance of the historical context and significance all coins and objects represent. Most others are only concerned with selling you, Ilya Zlobin is most interested in educating you on the subject, and providing the largest selection, most professional presentation and service for the best long-term value for collectors worldwide creating returning patrons sharing in the passion of ancient and world coin collecting for a lifetime.
How long until my order is shipped?
Orders are shipped by the next business day (after receipt of payment) most of the time.
How will I know when the order was shipped?
After your order has shipped, you will be left positive feedback, and that date could be used as a basis of estimating an arrival date. Any tracking number would be found under your 'Purchase history' tab.
USPS First Class mail takes about 3-5 business days to arrive in the U.S. International shipping times cannot be estimated as they vary from country to country.
Standard international mail to many countries
does not
include a tracking number, and can also be slow sometimes.
For a tracking number and signature confirmation, you may want to do Express Mail International Shipping, which costs more, however, is the fastest and most secure. Additionally you may be able to receive your order in as little as 3-5 business days using this method. For Express Mail International, it may be possible to place up to 10-15 items in one package (for the one shipping cost) as it is flat rate envelope, which may be the most cost-effective, secure and fastest way to receive items internationally. Send me a message about this and I can update your invoice should you want this method.
Getting your order to you, quickly and securely is a top priority and is taken seriously here.
Great care is taken in packaging and mailing every item securely and quickly.
Please be aware, I cannot take responsibility for any postal service delivery delays, especially for international packages as it may happen in rare instances.
What is a certificate of authenticity and what guarantees do you give that the item is authentic?
Each of the items sold here, is provided with a Certificate of Authenticity, and a Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity, issued by a world-renowned numismatic and antique expert that has identified over 57,000 ancient coins and has provided them with the same guarantee. You will be very happy with what you get with the COA; a professional presentation of the coin, with all of the relevant information and a picture of the coin you saw in the listing. Additionally, the coin is inside it's own protective coin flip (holder), with a 2x2 inch description of the coin matching the individual number on the COA.
On the free-market such a presentation alone, can be considered a - value all in itself, and it comes standard with your purchases from me,
FREE.
With every purchase, you are leveraging my many years of experience to get a more complete context and understanding of the piece of history you are getting. Whether your goal is to collect or give the item as a gift, coins presented like this could be more prized and valued higher than items that were not given such care and attention to.
Buy a coin today and own a piece of history, guaranteed.
Is there a money back guarantee?
I offer a 30 day unconditional money back guarantee. I stand behind my coins and would be willing to exchange your order for either store credit towards other coins, or refund, minus shipping expenses, within 30 days from the receipt of your order. My goal is to have the returning customers for a lifetime, and I am so sure in my coins, their authenticity, numismatic value and beauty, I can offer such a guarantee.
Is there a number I can call you with questions about my order?
You can contact me directly via ask seller a question and request my telephone number, or go to my About Me Page to get my contact information only in regards to items purchased on eBay.
When should I leave feedback?
Once you receive your order, please leave a positive feedback. Please don't leave any negative feedbacks, as it happens sometimes that people rush to leave feedback before letting sufficient time for their order to arrive. Also, if you sent an email, make sure to check for my reply in your messages before claiming that you didn't receive a response. The matter of fact is that any issues can be resolved, as reputation is most important to me. My goal is to provide superior products and quality of service.
How and where do I learn more about collecting ancient coins?
Visit the "Guide on How to Use My Store" for on an overview about using my store, with additional information and links to all other parts of my store which may include educational information on topics you are looking for.
You may also want to do a YouTube search for the term "ancient coin collecting" for educational videos on this topic.