-40%
SEPTIMIUS SEVERUS Ancient PHILIPPOPOLIS THRACE Tripod SERPENT Roman Coin i79411
$ 41.6
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
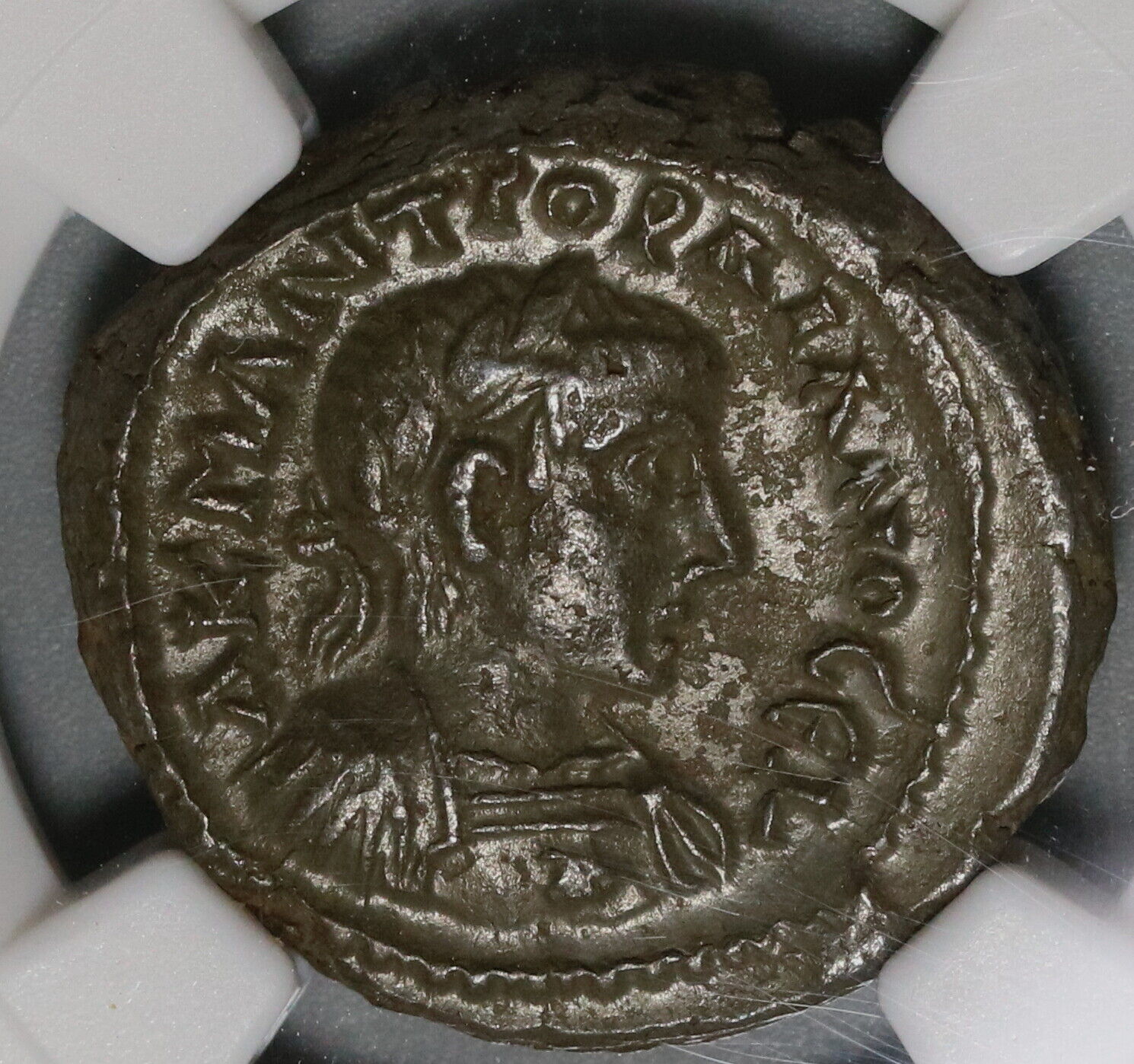
Item:i79411
Authentic Ancient Coin of:
Septimius Severus
-
Roman Emperor
: 193-211 A.D.
Bronze 18mm (4.01 grams) of
Philippopolis
in
Thrace
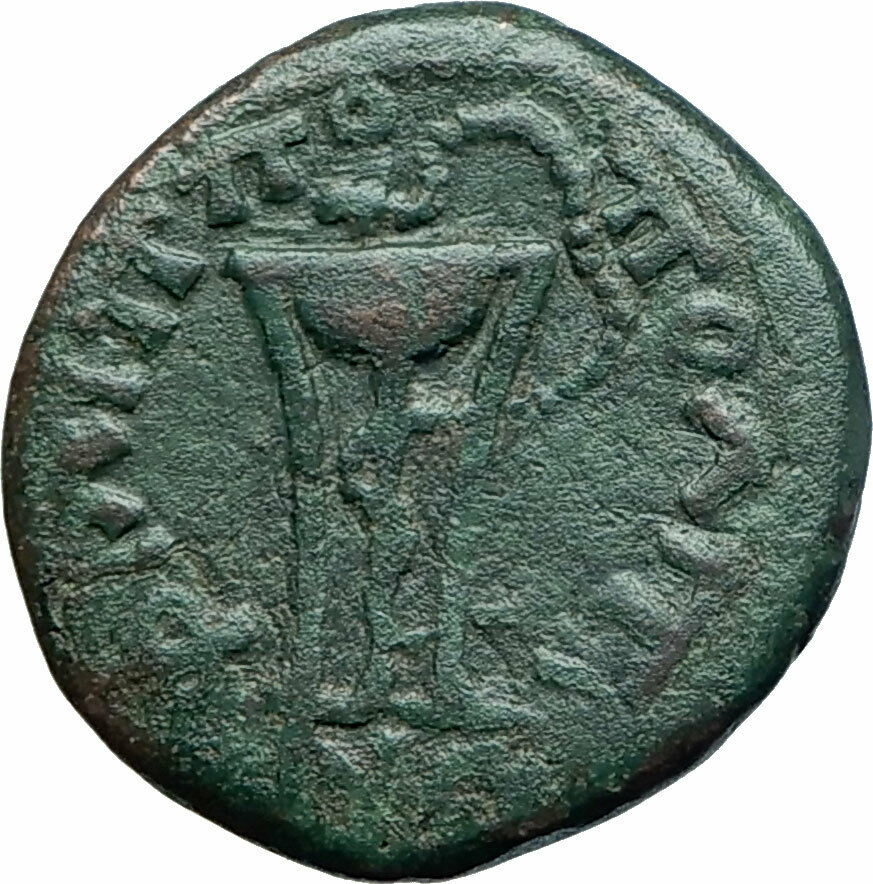
Laureate head of Septimius Severus right.
Tripod with serpent entwined around the central leg.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
A
sacrificial tripod
is a three-legged piece of religious furniture used for offerings or other ritual procedures. As a seat or stand, the tripod is the most stable furniture construction for uneven ground, hence its use is universal and ancient. It is particularly associated with Apollo and the Delphic oracle in ancient Greece, and the word "tripod" comes from the Greek meaning "three-footed".
The most famous tripod of ancient Greece was the
Delphic Tripod
from which the Pythian priestess took her seat to deliver the oracles of the deity. The seat was formed by a circular slab on the top of the tripod, on which a branch of laurel was deposited when it was unoccupied by the priestess. In this sense, by classical times the tripod was sacred to Apollo. According to the myth, Hercules went to the oracle of Delphi in order to ask what to do in order to be expiated from the murder of Iphitos. The oracle did not want to give him an omen. Then, the hero was enraged and he grabbed the tripod on which the Pythia sat in order to pronounce her oracles. Apollo tried to prevent him and this resulted in a fight between the god and the hero. Finally, Zeus had to intervene in order to end this quarrel.The mytheme of Heracles contesting with Apollo for the tripod appears in vase-paintings older than the oldest written literature. The oracle originally may have been related to the primal deity, the Earth. In the Geometric period, the tripods were fastened to the cauldrons they supported. In the Museum of Delphi there are fragments of such tripods, most distinctive of which is the one with a ring-shaped handle.
Another well-known tripod in Delphi was the Plataean Tripod; it was made from a tenth part of the spoils taken from the Persian army after the Battle of Plataea. This consisted of a golden basin, supported by a bronze serpent with three heads (or three serpents intertwined), with a list of the states that had taken part in the war inscribed on the coils of the serpent. The golden bowl was carried off by the Phocians during the Third Sacred War (356-346 BC); the stand was removed by the emperor Constantine to Constantinople in 324, where in modern Istanbul it still can be seen in the hippodrome, the
Atmeydanı
, although in damaged condition: the heads of the serpents have disappeared, however one is now on display at the nearby Istanbul Archaeology Museums. The inscription, however, has been restored almost entirely. Such tripods usually had three
ears
(rings which served as handles) and frequently had a central upright as support in addition to the three legs.
Tripods frequently are mentioned by Homer as prizes in athletic games and as complimentary gifts; in later times, highly decorated and bearing inscriptions, they served the same purpose. They appear also to be precious gifts for the guests, as in the case of the Phaeakes, who offered a cauldron and tripod to Odysseus.
Our guest has already packed up the clothes, wrought gold, and other valuables which you have brought for his acceptance;
let us now, therefore, present him further, each one of us, with a large tripod and a cauldron. We will recoup ourselves by the levy of a general rate; for private individuals cannot be expected to bear the burden of such a handsome present.
Odyssey, 13.10-15 [tr. S. Butler]
They also were used as dedicatory offerings to the deities, and in the dramatic contests at the Dionysia the victorious choregus (a wealthy citizen who bore the expense of equipping and training the chorus) received a crown and a tripod. He would either dedicate the tripod to some deity or set it upon the top of a marble structure erected in the form of a small circular temple in a street in Athens, called the
street of tripods,
from the large number of memorials of this kind. One of these, the Choragic Monument of Lysicrates, erected by him to commemorate his victory in a dramatic contest in 335 BC, still stands. The form of the victory tripod, now missing from the top of the Lysicrates monument, has been rendered variously by scholars since the 18th century.
Martin L. West writes that the Pythia at Delphi shows many traits of shamanistic practices, likely inherited or influenced from Central Asian practices. He cites her sitting in a cauldron on a tripod, while making her prophecies, her being in an ecstatic trance state, similar to shamans, and her utterings, unintelligible.
According to Herodotus (The Histories, I.144), the victory tripods were not to be taken from the temple sanctuary precinct, but left there as dedications.
Plovdiv
(Bulgarian: Пловдив) is the second-largest city in Bulgaria with a population of 380,683. Plovdiv's history spans some 6,000 years, with traces of a Neolithic settlement dating to roughly 4000 BC. It is the administrative center of Plovdiv Province in southern Bulgaria and three municipalities (Plovdiv, Maritsa and Rodopi) and Bulgaria's Yuzhen tsentralen planning region (NUTS II), as well as the largest and most important city in Northern Thrace and the wider international historical region of Thrace. The city is an important economic, transport, cultural and educational center.
Known in the West for most of its history by the Greek name
Philippopolis
, it was originally a Thracian settlement before becoming a major Roman city. In the Middle Ages, it retained its strategic regional importance, changing hands between the Byzantine and Bulgarian Empires. It came under Ottoman rule in the 14th century. In 1878, Plovdiv was made the capital of the autonomous Ottoman region of Eastern Rumelia; in 1885, it became part of Bulgaria with the unification of that region and the Principality of Bulgaria.
Plovdiv is situated in the southern part of the Plovdiv Plain on the two banks of the Maritsa River. The city has historically developed on seven syenite hills, some of which are 250 m high. Because of these seven hills, Plovdiv is often referred to in Bulgaria as "The City of the Seven Hills".
There are many remains preserved from Antiquity such as the Ancient amphitheatre, Roman odeon, Roman Stadium, the archaeological complex
Eirene
and others.
Plovdiv was given various names throughout its long history. It was originally a Thracian settlement by the name of
Eumolpias
. Philip II of Macedon conquered the area in 342-341 BC and renamed the city
Philippoupolis
(Greek: Φιλιππούπολις), of which the later Thracian name for the city,
Pulpu-deva
, is a reconstructed translation. After the Romans took control of the area, the city was named Latin:
Trimontium
, meaning the Three Hills. During the Middle Ages the city was known as Philippoupolis in Byzantine Greek and
Paldin
(Пълдин) or
Plavdiv
(Плъвдив) in Old Bulgarian, variations of the town's earlier Thracian name. The city was known as Philippopolis in Western Europe well into the early 20th century. The city was known as
Filibe
in Turkish during the Ottoman Empire.
Plovdiv has settlement traces dating from the Neolithic, roughly 4000 BC. Archaeologists have discovered fine pottery and other objects of everyday life from as early as the Neolithic Age, showing that in the end of the 4
th
millennium B.C. there already was an established settlement there. According to Ammianus Marcellinus, Plovdiv's written post-Bronze Age history lists it as a Thracian fortified settlement named Eumolpias. In 4th century BC the city was a centre of a trade fair (called
panegyreis
). In 342 BC, it was conquered by Philip II of Macedon, the father of Alexander the Great, who renamed it "Φιλιππόπολις",
Philippopolis
or "the city of Philip" in his own honour. Later, it was reconquered by the Thracians who called it
Pulpudeva
(a reconstructed translation of Philipopolis)
In 72 AD it was seized by the Roman general Terentius Varo Lukulus and was incorporated into the Roman Empire, where it was called
Trimontium
(
City of Three Hills
) and served as metropolis (capital) of the province of Thrace. It gained a city status in late 1st century. Trimontium was an important crossroad for the Roman Empire and was called "The largest and most beautiful of all cities" by Lucian. Although it was not the capital of the Province of Thrace, the city was the largest and most important centre in the province. In those times, the
Via Militaris
(or
Via Diagonalis
), the most important military road in the Balkans, passed through the city.
"This [Plovdiv] is the biggest and loveliest of all cities. Its beauty shines from faraway..."
Roman writer Lucian.
The Roman times were a period of growth and cultural excellence. The ancient ruins tell a story of a vibrant, growing city with numerous public buildings, shrines, baths, and theatres. The city had an advanced water system and sewerage. It was defended with a double wall. Many of those are still preserved and can be seen by tourists. Today only a small part of the ancient city has been excavated.
Septimius Severus
-
Roman Emperor
: 193-211 A.D.
Augustus: 193-211 A.D. | 193-198 A.D. Sole reign; 195-198 A.D.
Caracalla
as Caesar | 198-209 A.D. with
Caracalla
;
Geta
as Caesar | 209-211 A.D. with
Caracalla
and
Geta
Husband of
Julia Domna
| Father of
Caracalla
and
Geta
| Uncle of
Julia Soaemias
and
Julia Mamaea
| Great-uncle of
Elagabalus
and
Severus Alexander
| Brother-in-law of
Julia Maesa
| Father-in-law of
Plautilla
|
Lucius Septimius Severus
(or rarely
Severus I
) (April 11, 145/146-February 4, 211) was a Roman general, and Roman Emperor from April 14, 193 to 211. He was born in what is now the Berber part of Rome's historic Africa Province.
Septimius Severus was born and raised at Leptis Magna (modern Berber, southeast of Carthage, modern Tunisia). Severus came from a wealthy, distinguished family of equestrian rank. Severus was of Italian Roman ancestry on his mother's side and of Punic or Libyan-Punic ancestry on his father's. Little is known of his father, Publius Septimius Geta, who held no major political status but had two cousins who served as consuls under emperor Antoninus Pius. His mother, Fulvia Pia's family moved from Italy to North Africa and was of the Fulvius gens, an ancient and politically influential clan, which was originally of plebeian status. His siblings were a younger Publius Septimius Geta and Septimia Octavilla. Severus's maternal cousin was Praetorian Guard and consul Gaius Fulvius Plautianus.
In 172, Severus was made a Senator by the then emperor Marcus Aurelius. In 187 he married secondly Julia Domna. In 190 Severus became consul, and in the following year received from the emperor Commodus (successor to Marcus Aurelius) the command of the legions in Pannonia.
On the murder of Pertinax by the troops in 193, they proclaimed Severus Emperor at Carnuntum, whereupon he hurried to Italy. The former emperor, Didius Julianus, was condemned to death by the Senate and killed, and Severus took possession of Rome without opposition.
The legions of Syria, however, had proclaimed Pescennius Niger emperor. At the same time, Severus felt it was reasonable to offer Clodius Albinus, the powerful governor of Britannia who had probably supported Didius against him, the rank of Caesar, which implied some claim to succession. With his rearguard safe, he moved to the East and crushed Niger's forces at the Battle of Issus. The following year was devoted to suppressing Mesopotamia and other Parthian vassals who had backed Niger. When afterwards Severus declared openly his son Caracalla as successor, Albinus was hailed emperor by his troops and moved to Gallia. Severus, after a short stay in Rome, moved northwards to meet him. On February 19, 197, in the Battle of Lugdunum, with an army of 100,000 men, mostly composed of Illyrian, Moesian and Dacian legions, Severus defeated and killed Clodius Albinus, securing his full control over the Empire.
Emperor
Severus was at heart a soldier, and sought glory through military exploits. In 197 he waged a brief and successful war against the Parthian Empire in retaliation for the support given to Pescennius Niger. The Parthian capital Ctesiphon was sacked by the legions, and the northern half of Mesopotamia was restored to Rome.
His relations with the Roman Senate were never good. He was unpopular with them from the outset, having seized power with the help of the military, and he returned the sentiment. Severus ordered the execution of dozens of Senators on charges of corruption and conspiracy against him, replacing them with his own favorites.
He also disbanded the Praetorian Guard and replaced it with one of his own, made up of 50,000 loyal soldiers mainly camped at Albanum, near Rome (also probably to grant the emperor a kind of centralized reserve). During his reign the number of legions was also increased from 25/30 to 33. He also increased the number of auxiliary corps (
numerii
), many of these troops coming from the Eastern borders. Additionally the annual wage for a soldier was raised from 300 to 500
denarii
.
Although his actions turned Rome into a military dictatorship, he was popular with the citizens of Rome, having stamped out the rampant corruption of Commodus's reign. When he returned from his victory over the Parthians, he erected the Arch of Septimius Severus in Rome.
According to Cassius Dio, however, after 197 Severus fell heavily under the influence of his Praetorian Prefect, Gaius Fulvius Plautianus, who came to have almost total control of most branches of the imperial administration. Plautianus's daughter, Fulvia Plautilla, was married to Severus's son, Caracalla. Plautianus's excessive power came to an end in 205, when he was denounced by the Emperor's dying brother and killed. The two following
praefecti
, including the jurist Aemilius Papinianus, received however even larger powers.
Campaigns in Caledonia (Scotland)
Starting from 208 Severus undertook a number of military actions in Roman Britain, reconstructing Hadrian's Wall and campaigning in Scotland.
He reached the area of the Moray Firth in his last campaign in Caledonia, as was called Scotland by the Romans.. In 210 obtained a peace with the Picts that lasted practically until the final withdrawal of the Roman legions from Britain, before falling severely ill in Eboracum (York).
Death
He is famously said to have given the advice to his sons: "Be harmonious, enrich the soldiers, and scorn all other men" before he died at Eboracum on February 4, 211. Upon his death in 211, Severus was deified by the Senate and succeeded by his sons, Caracalla and Geta, who were advised by his wife Julia Domna. The stability Severus provided the Empire was soon gone under their reign.
Accomplishments and Record
Though his military expenditure was costly to the empire, Severus was the strong, able ruler that Rome needed at the time. He began a tradition of effective emperors elevated solely by the military. His policy of an expanded and better-rewarded army was criticized by his contemporary Dio Cassius and Herodianus: in particular, they pointed out the increasing burden (in the form of taxes and services) the civilian population had to bear to maintain the new army.
Severus was also distinguished for his buildings. Apart from the triumphal arch in the Roman Forum carrying his full name, he also built the Septizodium in Rome and enriched greatly his native city of Leptis Magna (including another triumphal arch on the occasion of his visit of 203).
Severus and Christianity
Christians were persecuted during the reign of Septimus Severus. Severus allowed the enforcement of policies already long-established, which meant that Roman authorities did not intentionally seek out Christians, but when people were accused of being Christians they could either curse Jesus and make an offering to Roman gods, or be executed. Furthermore, wishing to strengthen the peace by encouraging religious harmony through syncretism, Severus tried to limit the spread of the two quarrelsome groups who refused to yield to syncretism by outlawing conversion to Christianity or Judaism. Individual officials availed themselves of the laws to proceed with rigor against the Christians. Naturally the emperor, with his strict conception of law, did not hinder such partial persecution, which took place in Egypt and the Thebaid, as well as in Africa proconsularis and the East. Christian martyrs were numerous in Alexandria (cf. Clement of Alexandria,
Stromata
, ii. 20; Eusebius,
Church History
, V., xxvi., VI., i.). No less severe were the persecutions in Africa, which seem to have begun in 197 or 198 (cf. Tertullian's
Ad martyres
), and included the Christians known in the
Roman martyrology
as the martyrs of Madaura. Probably in 202 or 203 Felicitas and Perpetua suffered for their faith. Persecution again raged for a short time under the proconsul Scapula in 211, especially in Numidia and Mauritania. Later accounts of a Gallic persecution, especially at Lyon, are legendary. In general it may thus be said that the position of the Christians under Septimius Severus was the same as under the Antonines; but the law of this Emperor at least shows clearly that the rescript of Trajan had failed to execute its purpose.
Frequently Asked Questions
Mr. Ilya Zlobin
, world-renowned expert numismatist, enthusiast, author and dealer in authentic ancient Greek, ancient Roman, ancient Byzantine, world coins & more.
Who am I dealing with?
You are dealing with Ilya Zlobin, ancient coin expert, enthusiast, author and dealer with an online store having a selection of over 15,000 items with great positive feedback from verified buyers and over 10 years experience dealing with over 57,000 ancient and world coins and artifacts. Ilya Zlobin is an independent individual who has a passion for coin collecting, research and understanding the importance of the historical context and significance all coins and objects represent. Most others are only concerned with selling you, Ilya Zlobin is most interested in educating you on the subject, and providing the largest selection, most professional presentation and service for the best long-term value for collectors worldwide creating returning patrons sharing in the passion of ancient and world coin collecting for a lifetime.
How long until my order is shipped?
Orders are shipped by the next business day (after receipt of payment) most of the time.
How will I know when the order was shipped?
After your order has shipped, you will be left positive feedback, and that date could be used as a basis of estimating an arrival date. Any tracking number would be found under your 'Purchase history' tab.
USPS First Class mail takes about 3-5 business days to arrive in the U.S. International shipping times cannot be estimated as they vary from country to country.
Standard international mail to many countries
does not
include a tracking number, and can also be slow sometimes.
For a tracking number and signature confirmation, you may want to do Express Mail International Shipping, which costs more, however, is the fastest and most secure. Additionally you may be able to receive your order in as little as 3-5 business days using this method. For Express Mail International, it may be possible to place up to 10-15 items in one package (for the one shipping cost) as it is flat rate envelope, which may be the most cost-effective, secure and fastest way to receive items internationally. Send me a message about this and I can update your invoice should you want this method.
Getting your order to you, quickly and securely is a top priority and is taken seriously here.
Great care is taken in packaging and mailing every item securely and quickly.
Please be aware, I cannot take responsibility for any postal service delivery delays, especially for international packages as it may happen in rare instances.
What is a certificate of authenticity and what guarantees do you give that the item is authentic?
Each of the items sold here, is provided with a Certificate of Authenticity, and a Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity, issued by a world-renowned numismatic and antique expert that has identified over 57,000 ancient coins and has provided them with the same guarantee. You will be very happy with what you get with the COA; a professional presentation of the coin, with all of the relevant information and a picture of the coin you saw in the listing. Additionally, the coin is inside it's own protective coin flip (holder), with a 2x2 inch description of the coin matching the individual number on the COA.
On the free-market such a presentation alone, can be considered a - value all in itself, and it comes standard with your purchases from me,
FREE.
With every purchase, you are leveraging my many years of experience to get a more complete context and understanding of the piece of history you are getting. Whether your goal is to collect or give the item as a gift, coins presented like this could be more prized and valued higher than items that were not given such care and attention to.
Buy a coin today and own a piece of history, guaranteed.
Is there a money back guarantee?
I offer a 30 day unconditional money back guarantee. I stand behind my coins and would be willing to exchange your order for either store credit towards other coins, or refund, minus shipping expenses, within 30 days from the receipt of your order. My goal is to have the returning customers for a lifetime, and I am so sure in my coins, their authenticity, numismatic value and beauty, I can offer such a guarantee.
Is there a number I can call you with questions about my order?
You can contact me directly via ask seller a question and request my telephone number, or go to my
About Me Page
to get my contact information only in regards to items purchased on eBay.
When should I leave feedback?
Once you receive your order, please leave a positive feedback. Please don't leave any negative feedbacks, as it happens sometimes that people rush to leave feedback before letting sufficient time for their order to arrive. Also, if you sent an email, make sure to check for my reply in your messages before claiming that you didn't receive a response. The matter of fact is that any issues can be resolved, as reputation is most important to me. My goal is to provide superior products and quality of service.
How and where do I learn more about collecting ancient coins?
Visit the
"Guide on How to Use My Store"
for on an overview about using my store, with additional information and links to all other parts of my store which may include educational information on topics you are looking for.