-40%
GORDIAN III 238AD Odessos Thrace GREAT GOD DERZELAS Ancient Roman Coin i50920
$ 132
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
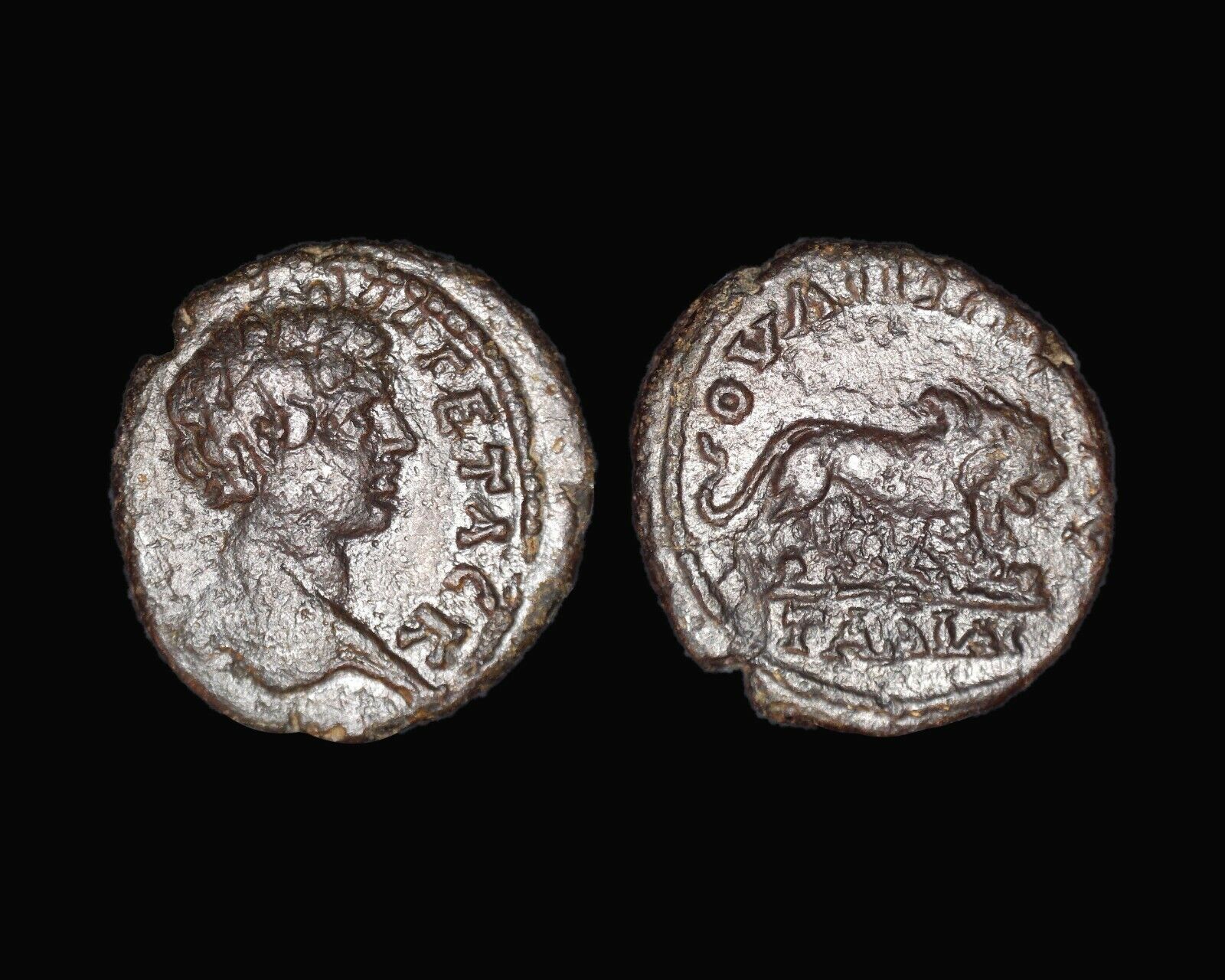
Item:i50920
Authentic Ancient Coin of:
Gordian III -
Roman Emperor
: 238-244 A.D. -
Bronze 26mm (10.42 grams) of
<="" font="" face="Times New Roman" color="#000000"> Odessos
in Thrace
Reference: Varbanov, 4451 var.
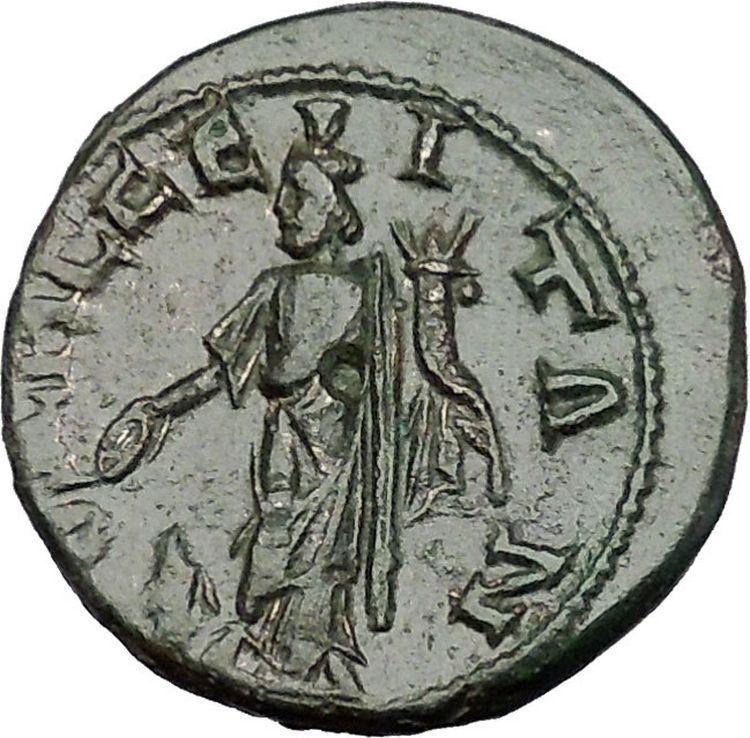
AVT M ANT ╬ō╬¤╬Ī╬ö╬Ö╬æ╬Ø╬¤C┬Ā AV╬ō, Laureate, draped and cuirassed bust right.
O╬öHCCEIT╬®N, the Great God, Derzelas
,
of Odessos standing left, sacrificing from patera over altar on left and holding cornucopia.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
Derzelas (
Darzalas
) was a
Dacian
or
Thracian
chthonic
god of abundance and the underworld, health and human spirit's vitality, probably related with gods such as
Hades
,
Zalmoxis
,
Gebeleizis
.
Darzalas was the Great God of
Hellenistic
Odessos
(modern
Varna
) and was frequently depicted on its
coinage
from the 3rd century BCE to the 3rd century CE and portrayed in numerous
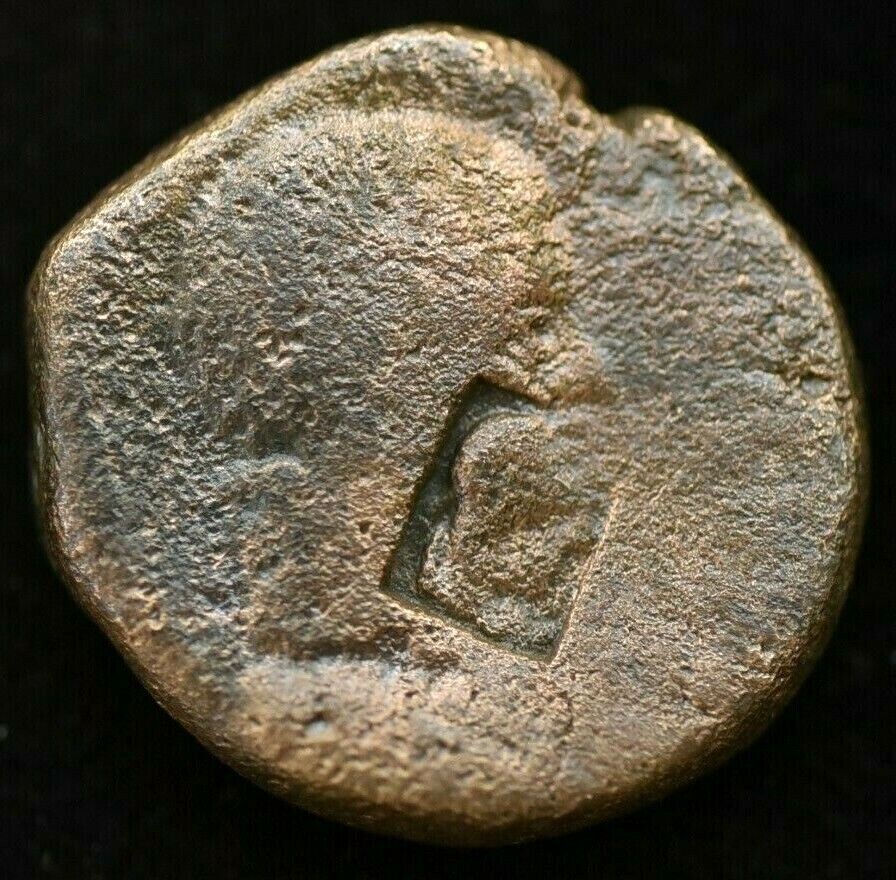
terra cotta
figurines, as well as in a rare 4th century BC lead one (
photo
), found in the city. Darzalas was often
depicted
in
himation
, holding
cornucopiae
with
altars
by his side. There was a temple dedicated to him with a cult statue, and games (
Darzaleia
) were held in his honor every five years, possibly attended by
Gordian III
in 238 AD.
Another temple dedicated to Derzelas was built at
Histria (Sinoe)
- a Greek colony, on the shore of the
Black Sea
in the 3rd century BC.
Darzalas Peak
on
Trinity Peninsula
in
Antarctica
The region of ancient
Thracee
was populated by
Thracians
by 1000 BCE.
Miletian
Greeks
founded the
apoikia
(trading post) of Odess├▓s towards the end of the 7th century BC (the earliest Greek archaeological material is dated 600ŌĆō575 BCE), or, according to
Pseudo-Scymnus
,
in the time of
Astyages
(here, usually 572ŌĆō570 BCE is suggested), within an earlier Thracian settlement. The name
Odessos
was pre-Greek, arguably of
Carian
origin. A member of the Pontic
Pentapolis
, Odessos was a mixed communityŌĆöcontact zone between the
Ionian
Greeks
and the
Thracian
tribes (
Getae
,
Krobyzoi
,
Terizi
) of the
hinterland
. Excavations at nearby Thracian sites have shown uninterrupted occupation from the 7th to the 4th century and close commercial relations with the colony. The Greek alphabet has been applied to inscriptions in
Thracian
since at least the 5th century BCE; the city worshipped a Thracian great god whose cult survived well into the
Roman
period.
See also: Derzelas
Odessos was included in the assessment of the
Delian league
of 425 BCE. In 339 BCE, it was unsuccessfully besieged by
Philip II
(priests of the Getae persuaded him to conclude a treaty) but surrendered to
Alexander the Great
in 335 BCE, and was later ruled by his
diadochus
Lysimachus
, against whom it rebelled in 313 BC as part of a coalition with other Pontic cities and the Getae. The Roman city,
Odessus
, first included into the
Praefectura orae maritimae
and then in 15 CE annexed to the province of
Moesia
(later
Moesia Inferior
), covered 47 hectares in present-day central Varna and had prominent public baths,
Thermae
, erected in the late 2nd century AD, now the largest Roman remains in Bulgaria (the building was 100┬Ām (328.08┬Āft) wide, 70┬Ām (229.66┬Āft) long, and 25┬Ām (82.02┬Āft) high) and fourth-largest known Roman baths in Europe. Major athletic games were held every five years, possibly attended by
Gordian III
in 238 CE.
Odessus was an early
Christian
centre, as testified by ruins of ten early basilicas, a
monophysite
monastery, and indications that one of the
Seventy Disciples
,
Ampliatus
, follower of
Saint Andrew
(who, according to the
Bulgarian Orthodox Church
legend, preached in the city in 56 CE), served as bishop there. In 6th-century CE imperial documents, it was referred to as "holiest city,"
sacratissima civitas
. In 442 CE, a peace treaty between
Theodosius II
and
Attila
was done at Odessus. In 513, it became a focal point of the
Vitalian
revolt. In 536,
Justinian I
made it the seat of the
Quaestura exercitus
ruled by a
prefect of Scythia
or
quaestor Justinianus
and including Lower Moesia,
Scythia
, Caria, the
Aegean Islands
and Cyprus; later, the military camp outside Odessus was the seat of another senior Roman commander,
magister militum per Thracias
.
It has been suggested that the 681 peace treaty with the
Byzantine Empire
that established the new Bulgarian state was concluded at Varna and the first Bulgarian capital south of the Danube may have been provisionally located in its vicinityŌĆöpossibly in an ancient city near Lake Varna's north shore named Theodorias (╬ś╬Ą╬┐╬┤ŽēŽü╬╣╬¼Žé) by Justinian IŌĆöbefore it moved to
Pliska
70 kilometres (43 miles) to the west. Asparukh fortified the Varna river lowland by a rampart against a possible Byzantine landing; the
Asparuhov val
(Asparukh's Wall) is still standing. Numerous 7th-century
Bulgar
settlements have been excavated across the city and further west; the ; the Varna lakes north shores, of all regions, were arguably most densely populated by Bulgars. It has been suggested that Asparukh was aware of the importance of the Roman military camp (
campus tribunalis
) established by Justinian I outside Odessus and considered it (or its remnants) as the legitimate seat of power for both Lower Moesia and Scythia.
Marcus Antonius Gordianus Pius
(
January 20
,
225
ŌĆō
February 11
,
244
), known in
English
as
Gordian III
,
was
Roman Emperor
from 238 to 244. Gordian was the son of
Antonia Gordiana
and his father was an unnamed Roman Senator who died before 238. Antonia Gordiana was the daughter of Emperor
Gordian I
and younger sister of Emperor
Gordian II
. Very little is known on his early life before becoming Roman Emperor. Gordian had assumed the name of his maternal grandfather in 238.
Following the murder of emperor
Alexander Severus
in Moguntiacum (modern
Mainz
), the capital of the
Roman province
Germania Inferior
,
Maximinus Thrax
was acclaimed emperor, despite strong opposition of the
Roman senate
and the majority of the population. In response to what was considered in Rome as a rebellion, Gordian's grandfather and uncle, Gordian I and II, were proclaimed joint emperors in the
Africa Province
. Their revolt was suppressed within a month by Cappellianus, governor of
Numidia
and a loyal supporter of Maximinus Thrax. The elder Gordians died, but public opinion cherished their memory as peace loving and literate men, victims of Maximinus' oppression.
Pupienus
and
Balbinus
as joint emperors. These senators were not popular men and the population of Rome was still shocked by the elder Gordian's fate, so that the Senate decided to take the teenager Gordian, rename him Marcus Antonius Gordianus as his grandfather, and raise him to the rank of
Caesar
and imperial heir.
Pupienus
and
Balbinus
defeated Maximinus, mainly due to the defection of several
legions
, namely the
Parthica
II
who assassinated Maximinus. But their joint reign was doomed from the start with popular riots, military discontent and even an enormous fire that consumed Rome in June 238. On
July 29
, Pupienus and Balbinus were killed by the
Praetorian guard
and Gordian proclaimed sole emperor.
Rule
Due to Gordian's age, the imperial government was surrendered to the aristocratic families, who controlled the affairs of Rome through the senate. In 240,
Sabinianus
revolted in the African province, but the situation was dealt quickly. In 241, Gordian was married to Furia Sabinia
Tranquillina
, daughter of the newly appointed praetorian prefect,
Timesitheus
. As chief of the Praetorian guard and father in law of the emperor, Timesitheus quickly became the
de facto
ruler of the Roman empire.
In the 3rd century, the Roman frontiers weakened against the Germanic tribes across the
Rhine
and
Danube
, and the
Sassanid
kingdom across the
Euphrates
increased its own attacks. When the Persians under
Shapur I
invaded
Mesopotamia
, the young emperor opened the doors of the
Temple of Janus
for the last time in Roman history, and sent a huge army to the East. The Sassanids were driven back over the Euphrates and defeated in the
Battle of Resaena
(243). The campaign was a success and Gordian, who had joined the army, was planning an invasion of the enemy's territory, when his father-in-law died in unclear circumstances. Without Timesitheus, the campaign, and the emperor's security, were at risk.
Marcus Julius Philippus, also known as
Philip the Arab
, stepped in at this moment as the new Praetorian Prefect and the campaign proceeded. In the beginning of 244, the Persians counter-attacked. Persian sources claim that a battle was fought (
Battle of Misiche
) near modern
Fallujah
(
Iraq
) and resulted in a major Roman defeat and the death of Gordian III. Roman sources do not mention this battle and suggest that Gordian died far away, upstream of the Euphrates. Although ancient sources often described Philip, who succeeded Gordian as emperor, as having murdered Gordian at Zaitha (Qalat es Salihiyah), the cause of Gordian's death is unknown.
Gordian's youth and good nature, along with the deaths of his grandfather and uncle and his own tragic fate at the hands of another usurper, granted him the everlasting esteem of the Romans. Despite the opposition of the new emperor, Gordian was deified by the Senate after his death, in order to appease the population and avoid riots.
="">
Frequently Asked Questions
How long until my order is shipped?
Depending on the volume of sales, it may take up to 5 business days for shipment of your order after the receipt of payment.
How will I know when the order was shipped?
After your order has shipped, you will be left positive feedback, and that date should be used as a basis of estimating an arrival date.
After you shipped the order, how long will the mail take?
USPS First Class mail takes about 3-5 business days to arrive in the U.S., international shipping times cannot be estimated as they vary from country to country. I am not responsible for any USPS delivery delays, especially for an international package.
What is a certificate of authenticity and what guarantees do you give that the item is authentic?
Each of the items sold here, is provided with a Certificate of Authenticity, and a Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity, issued by a world-renowned numismatic and antique expert that has identified over 10000 ancient coins and has provided them with the same guarantee. You will be quite happy with what you get with the COA; a professional presentation of the coin, with all of the relevant information and a picture of the coin you saw in the listing.
Compared to other certification companies, the certificate of authenticity is a -50 value. So buy a coin today and own a piece of history, guaranteed.
Is there a money back guarantee?
I offer a 30 day unconditional money back guarantee. I stand behind my coins and would be willing to exchange your order for either store credit towards other coins, or refund, minus shipping expenses, within 30 days from the receipt of your order. My goal is to have the returning customers for a lifetime, and I am so sure in my coins, their authenticity, numismatic value and beauty, I can offer such a guarantee.
Is there a number I can call you with questions about my order?
You can contact me directly via ask seller a question and request my telephone number, or go to my About Me Page to get my contact information only in regards to items purchased on eBay.
When should I leave feedback?
Once you receive your order, please leave a positive. Please don't leave any negative feedbacks, as it happens many times that people rush to leave feedback before letting sufficient time for the order to arrive. Also, if you sent an email, make sure to check for my reply in your messages before claiming that you didn't receive a response. The matter of fact is that any issues can be resolved, as reputation is most important to me. My goal is to provide superior products and quality of service.