-40%
FAUSTINA I wife of ANTONINUS PIUS Sardes Lydia Aphrodite Rare Roman Coin i52342
$ 200.64
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
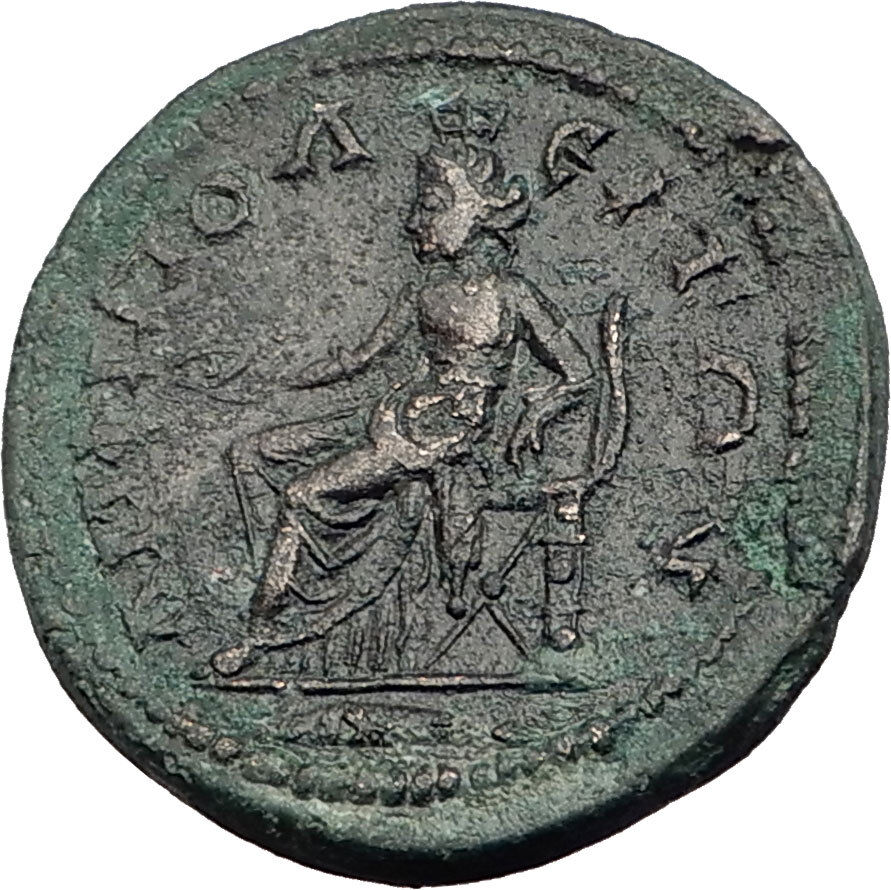
Item:i52342
Authentic Ancient Coin of:
Faustina I
- Roman Empress Wife of Roman Emperor
Antoninus Pius
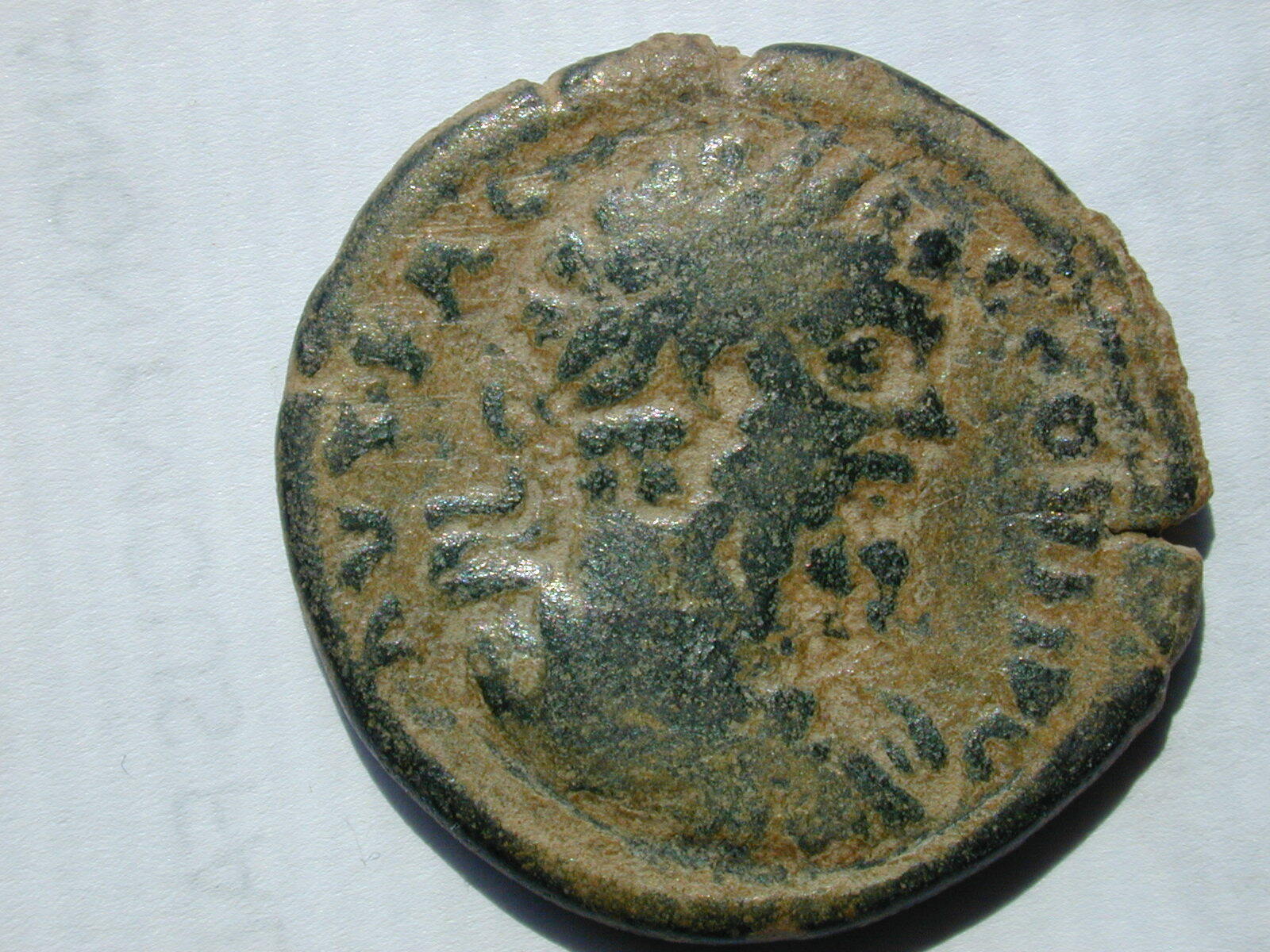
Bronze 18mm (4.98 grams) of
Sardes in Lydia
Reference: Mionnet IV, 720;Â Paris 1240
FAYCT
Є
INA C
Є
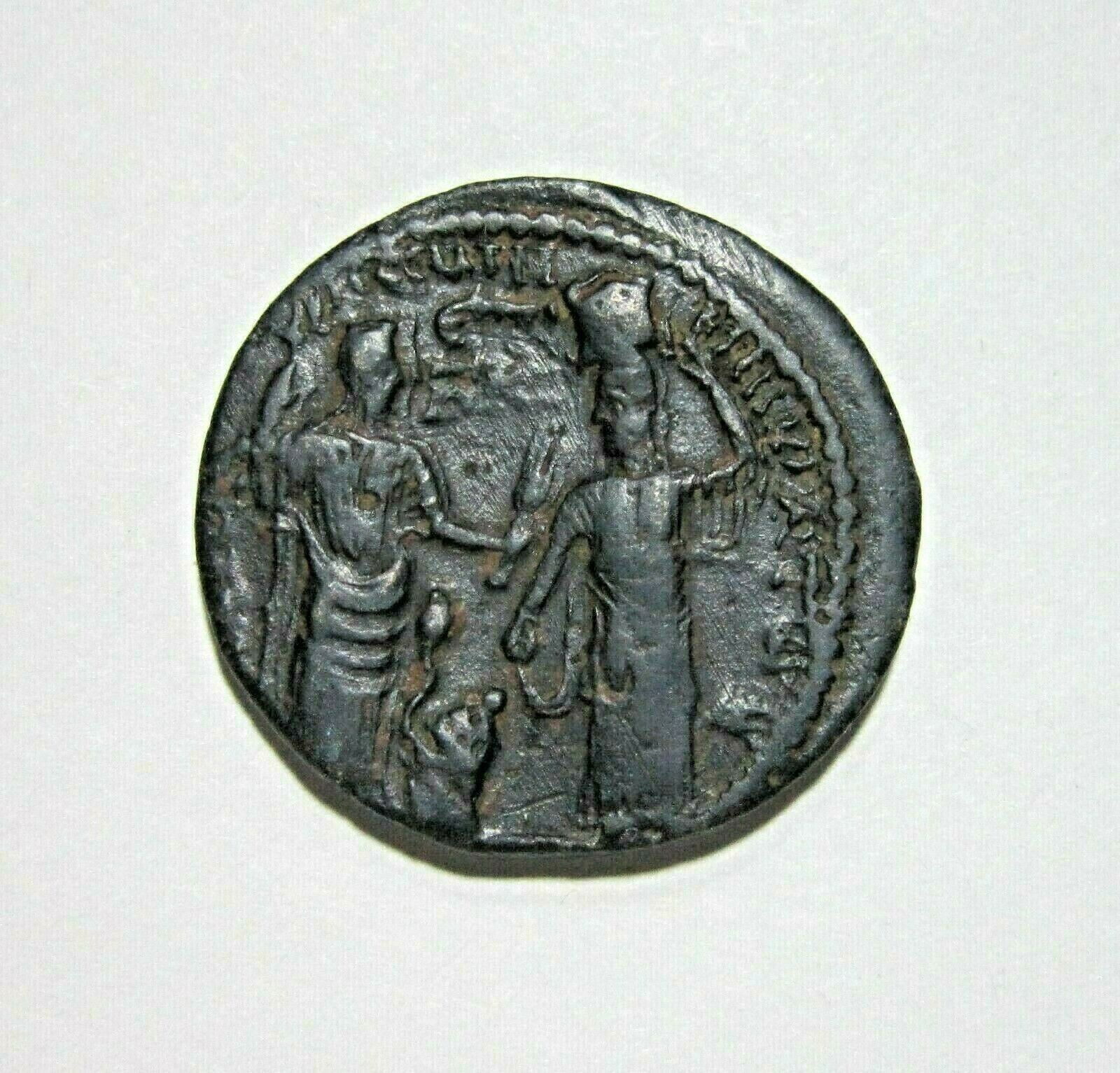
BACTH, draped bust right.
CAP
Δ
IAN
Ω
N, Aphrodite standing left, holding apple and scepter.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
Aphrodite
is the
Greek
goddess
of
love
,
beauty
, and
sexuality
. Her
Roman equivalent
is the goddess
Venus
. Historically, her cult in Greece was imported from, or influenced by, the
cult of
Astarte
in
Phoenicia
.
According to
Hesiod
's
Theogony
, she was born when
Cronus
cut off
Uranus
' genitals and threw them into the sea, and from the sea foam (
aphros
) arose Aphrodite.
Because of her beauty other gods feared that jealousy would interrupt the peace among them and lead to war, and so
Zeus
married her to
Hephaestus
, who was not viewed as a threat. Aphrodite had many lovers, both gods like
Ares
, and men like
Anchises
. Aphrodite also became instrumental in the
Eros and Psyche
legend, and later was both
Adonis
' lover and his surrogate mother. Many lesser beings were said to be children of Aphrodite.
Cytherea (
Lady of Cythera
) and
Cypris
(
Lady of Cyprus
) after the two cult-sites,
Cythera
and
Cyprus
, which claimed her birth.
Myrtles
,
doves
,
sparrows
,
horses
, and
swans
are sacred to her. The Greeks further identified the Ancient Egyptian goddess
Hathor
with Aphrodite.
[4]
Aphrodite also has many other local names, such as Acidalia, Cytherea and Cerigo, used in specific areas of Greece. Each goddess demanded a slightly different cult but Greeks recognized in their overall similarities the one Aphrodite. Attic philosophers of the fourth century separated a celestial Aphrodite (Aprodite Urania) of transcendent principles with the common Aphrodite of the people (Aphrodite Pandemos).
Sardis
or
Sardes
was an ancient city at the location of modern
Sart
(Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005) in
Turkey
's
Manisa Province
. Sardis was the capital of the ancient kingdom of
Lydia
, one of the important cities of the
Persian Empire
, the seat of a
proconsul
under the
Roman Empire
, and the metropolis of the province Lydia in later Roman and
Byzantine
times. As one of the
Seven churches of Asia
, it was addressed by the author John of the
Book of Revelation
in the Holy Bible in terms which seem to imply that its population was notoriously soft and fainthearted. Its importance was due, first to its military strength, secondly to its situation on an important highway leading from the interior to the
Aegean
coast, and thirdly to its commanding the wide and fertile plain of the
Hermus
..
Geography
Sardis was situated in the middle of
Hermus
valley, at the foot of
Mount Tmolus
, a steep and lofty spur which formed the citadel. It was about 4 kilometres (2.5Â mi) south of the Hermus. Today, the site is located by the present day village of
Sart
, near
Salihli
in the Manisa province of Turkey, close to the
Ankara
-
Ä°zmir
highway (approximately 72 kilometres (45Â mi) from
Ä°zmir
). The part of remains including the bath-gymnasium complex, synagogue and Byzantine shops is open to visitors year-round.
History
The earliest reference to Sardis is in the
The Persians
of
Aeschylus
(472Â BC); in the
Iliad
, the name Hyde seems to be given to the city of the
Maeonian
(i.e.
Lydian
) chiefs, and in later times Hyde was said to be the older name of Sardis, or the name of its
citadel
. It is, however, more probable that Sardis was not the original capital of the Maeonians, but that it became so amid the changes which produced the powerful
Lydian empire
of the 8th century BC.
The city was captured by the
Cimmerians
in the 7th century BC, by the
Persians
in the 6th, by the
Athenians
in the 5th, and by
Antiochus III the Great
at the end of the 3rd century BC. In the Persian era, Sardis was conquered by
Cyrus the Great
and formed the end station for the Persian
Royal Road
which began in
Persepolis
, capital of
Persia
. During the
Ionian Revolt
, the
Athenians
burnt down the city. Sardis remained under Persian domination until it surrendered to
Alexander the Great
in 334Â BC.
The early Lydian kingdom was very advanced in the industrial arts and Sardis was the chief seat of its manufactures. The most important of these trades was the manufacture and dyeing of delicate woolen stuffs and carpets. The stream
Pactolus
which flowed through the market-place "carried golden sands" in early antiquity, which was in reality gold dust out of
Mount Tmolus
. It was during the reign of King
Croesus
that the
metallurgists
of Sardis discovered the secret of separating
gold
from
silver
, thereby producing both metals of a purity never known before. This was an economic revolution, for while gold nuggets panned or mined were used as currency, their purity was always suspect and a hindrance to trade. Such nuggets or coinage were naturally occurring alloys of gold and silver known as
electrum
and one could never know how much of it was gold and how much was silver. Sardis now could mint nearly pure silver and gold coins, the value of which could be—and was—trusted throughout the known world. This revolution made Sardis rich and
Croesus
' name synonymous with wealth itself. For this reason, Sardis is famed in history as the place where modern
currency
was invented.
Disaster came to the great city under the reign of the emperor
Tiberius
, when in
AD 17, Sardis was destroyed by an earthquake
, but it was rebuilt. It was one of the great cities of western
Asia Minor
until the later
Byzantine
period.
Later, trade and the organization of commerce continued to be sources of great wealth. After
Constantinople
became the capital of the East, a new road system grew up connecting the provinces with the capital. Sardis then lay rather apart from the great lines of communication and lost some of its importance. It still, however, retained its titular supremacy and continued to be the seat of the
metropolitan bishop
of the province of Lydia, formed in AD 295. It was enumerated as third, after
Ephesus
and <="" font="" color="#000000">="">
<="" font="" color="#000000">, in the list of cities of the Thracesion
thema
given by
Constantine Porphyrogenitus
in the 10th century. However, over the next four centuries it was in the shadow of the provinces of Magnesia-upon-Sipylum and Philadelphia, which retained their importance in the region.
<="" font="" color="#000000">
After 1071 the Hermus valley began to suffer from the inroads of the
Seljuk Turks
but the Byzantine general
John Doukas
reconquered the city in 1097, the successes of the general Philokales in 1118 relieved the district from later Turkish pressure and the ability of the
Comneni
dynasty together with the gradual decay of the
Seljuk Sultanate of Rum
meant that it remained under Byzantine dominion. When
Constantinople
was taken by the
Venetians
and
Franks
in 1204 Sardis came under the rule of the Byzantine
Empire of Nicea
. However once the Byzantines retook Constantinople in 1261, Sardis with the entire
Asia Minor
was neglected and the region eventually fell under the control of Ghazi (
Ghazw
) emirs, the
Cayster
valleys and a fort on the citadel of Sardis was handed over to them by treaty in 1306. The city continued its decline until its capture (and probable destruction) by the
Mongol
warlord
Timur
in 1402.
Annia Galeria Faustina
, more familiarly referred to as
Faustina the Elder
(
Latin
:
Faustina Major
; born
September 21
about 100, died October or November 140), was a Roman Empress and wife of
Roman Emperor
Antoninus Pius
.
Faustina was the only known daughter of consul and prefect
Marcus Annius Verus
and
Rupilia
Faustina. Her brothers were consul
Marcus Annius Libo
and
praetor
Marcus Annius Verus
. Her maternal aunts perhaps were Roman Empress
Vibia Sabina
,
Matidia Minor
. Her paternal grandfather had the same name as her father and her maternal grandparents possibly were
Salonina Matidia
(niece of Roman Emperor
Trajan
) and suffect consul
Lucius Scribonius Libo Rupilius Frugi Bonus
. Faustina was born and raised in
Rome
.
As a private citizen, she married Antoninus Pius between 110 and 115. Faustina and Antoninus had a very happy marriage. Faustina bore Antoninus four children, two sons and two daughters. They were:
Marcus Aurelius Fulvius Antoninus (died before 138); his sepulchral inscription has been found at the Mausoleum of Hadrian in Rome.
Marcus Galerius Aurelius Antoninus (died before 138); his sepulchral inscription has been found at the Mausoleum of Hadrian in Rome. His name appears on a Greek Imperial coin.
Aurelia Fadilla (died in 135); she married Aelius Lamia Silvanus or Syllanus. She appears to have had no children with her husband and her sepulchral inscription has been found in
Italyy
Annia Galeria Faustina Minor or
Faustina the Younger
(between 125-130-175), a future Roman Empress; she married her maternal cousin, future Roman Emperor
Marcus Aurelius
. She was the only child who survived to adulthood.
On
July 10
,
138
, her uncle emperor
Hadrian
had died and her husband became the new emperor. Antoninus was Hadrian's adopted son and heir. Faustina became Roman Empress and the senate accorded her the title of
Augusta
. Faustina as an empress was well respected and this beautiful woman was renowned for her wisdom. The
Augustan History
impugned her character, criticizing her as having "excessive frankness" and "levity". However, this doesn’t appear to be the case with her character. Throughout her life, Faustina as a private citizen and an empress was involved in assisting with charities, assisting the poor and sponsoring and assisting in the education of Roman children, particularly of Roman girls.
She can be viewed as one of the most moral, stable and respected empresses in the history of the <="" font="" color="#000000">="">
<="" font="" color="#000000">. When Faustina died, Antoninus was in complete mourning for Faustina.
<="" font="" color="#000000">
Antoninus did the following in memory of his loving wife:
Deified her
as a goddess (her apotheosis was portrayed on an
honorary column
)
Had
a temple
built in the
Roman Forum
in her name, with priestesses in the temple.
Had various coins with her portrait struck in her honor. These coins were inscribed
DIVA FAVSTINA
("Divine Faustina") and were elaborately decorated.
Founded a charity called
Puellae Faustinianae
or
Girls of Faustina
, which assisted orphaned girls.
Created a new
alimenta
(see
Grain supply to the city of Rome
).
In 2008, archaeologists digging at the ancient site of
Sagalassos
in
Turkey
discovered a colossal marble head which is believed to be that of Faustina.
="">="">="">="">
Frequently Asked Questionss
How long until my order is shipped?:
Depending on the volume of sales, it may take up to 5 business days for shipment of your order after the receipt of payment.
How will I know when the order was shipped?:
After your order has shipped, you will be left positive feedback, and that date should be used as a basis of estimating an arrival date.
After you shipped the order, how long will the mail take?
USPS First Class mail takes about 3-5 business days to arrive in the U.S., international shipping times cannot be estimated as they vary from country to country. I am not responsible for any USPS delivery delays, especially for an international package.
What is a certificate of authenticity and what guarantees do you give that the item is authentic?
Each of the items sold here, is provided with a Certificate of Authenticity, and a Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity, issued by a world-renowned numismatic and antique expert that has identified over 10000 ancient coins and has provided them with the same guarantee. You will be quite happy with what you get with the COA; a professional presentation of the coin, with all of the relevant information and a picture of the coin you saw in the listing.
Compared to other certification companies, the certificate of authenticity is a -50 value. So buy a coin today and own a piece of history, guaranteed.
Is there a money back guarantee?
I offer a 30 day unconditional money back guarantee. I stand behind my coins and would be willing to exchange your order for either store credit towards other coins, or refund, minus shipping expenses, within 30 days from the receipt of your order. My goal is to have the returning customers for a lifetime, and I am so sure in my coins, their authenticity, numismatic value and beauty, I can offer such a guarantee.
Is there a number I can call you with questions about my order?
You can contact me directly via ask seller a question and request my telephone number, or go to my About Me Page to get my contact information only in regards to items purchased on eBay.
When should I leave feedback?
Once you receive your order, please leave a positive. Please don't leave any negative feedbacks, as it happens many times that people rush to leave feedback before letting sufficient time for the order to arrive. Also, if you sent an email, make sure to check for my reply in your messages before claiming that you didn't receive a response. The matter of fact is that any issues can be resolved, as reputation is most important to me. My goal is to provide superior products and quality of service.