-40%
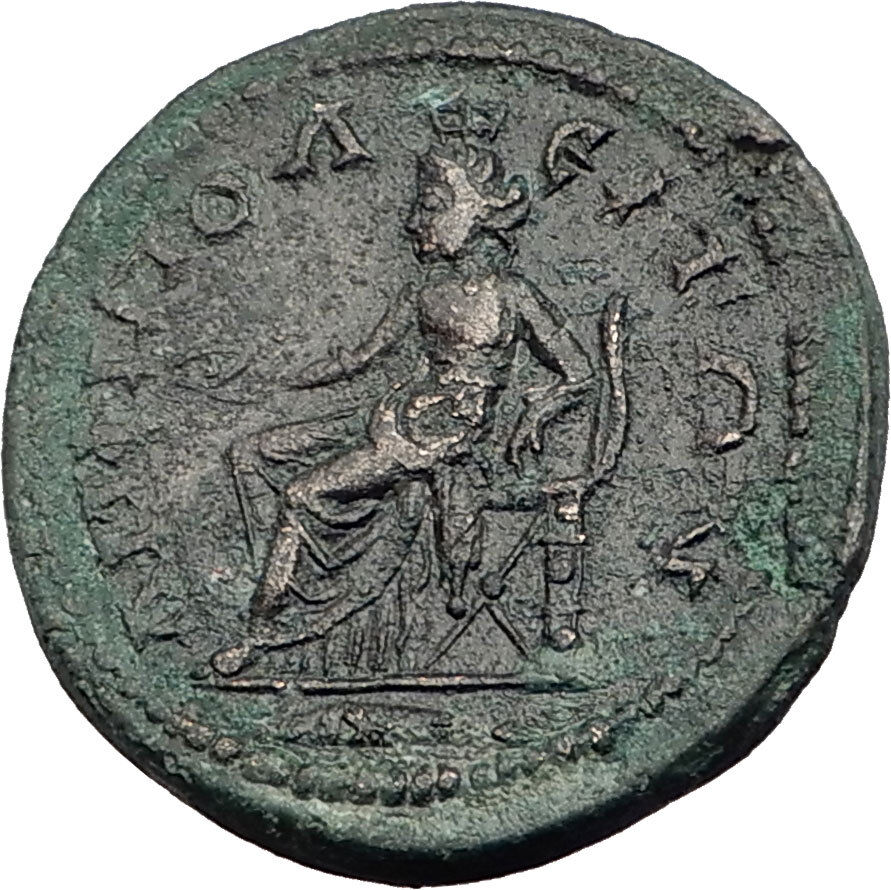
CARACALLA Nicopolis ad Istrum Rare Ancient Roman Coin Temple of Serapis i48475
$ 73.92
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Item:i48475
Authentic Ancient Coin of:
Caracalla
-
Roman Emperor
: 198-217 A.D. -
Bronze 27mm (12.19 grams) of
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman"> Nicopolis ad Istrum in Moesia Inferior
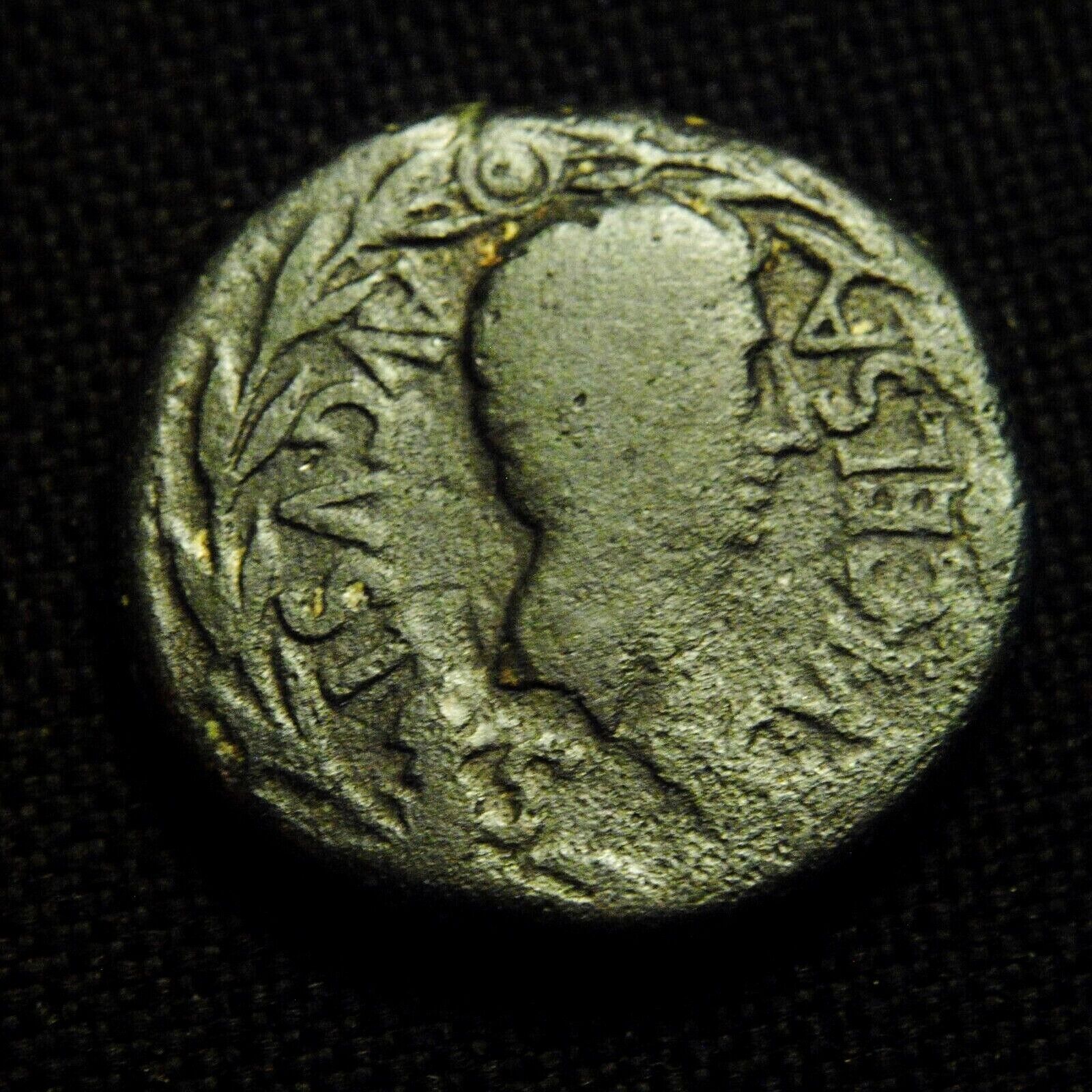
Laureate, draped and cuirassed bust right.
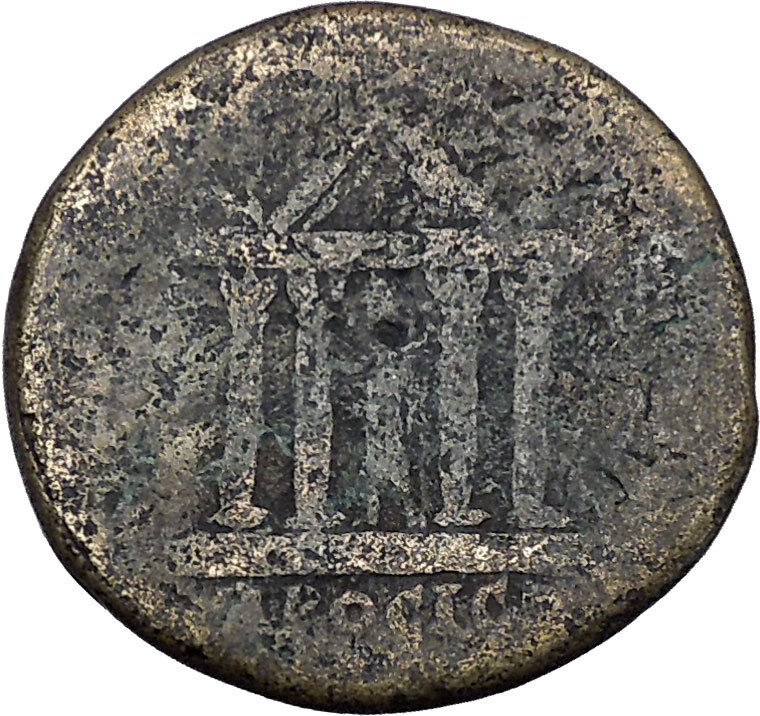
Tetrastyle (four-column) temple with statue of Serapis within.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
Serapis
is a Graeco-Egyptian god. Serapis was devised during the 3rd century BC on the orders of
Ptolemy I of Egypt
as a means to unify the Greeks and Egyptians in his realm. The god was depicted as Greek in appearance, but with Egyptian trappings, and combined iconography from a great many cults, signifying both abundance and resurrection. A
serapeum
(Greek
serapeion
) was any temple or religious precinct devoted to Serapis. The
cultus
of Serapis was spread as a matter of deliberate policy by the
Ptolemaic kings
, who also built an immense Serapeum in Alexandria.
Serapis continued to increase in popularity during the
Roman period
, often replacing
Osiris
as the consort of
Isis
in temples outside Egypt. In 389, a mob led by the
Patriarch
Theophilus of Alexandria
destroyed the Alexandrian Serapeum, but the cult survived until all forms of religion other than
Nicene Christianity
were suppressed or abolished under
Theodosius I
in 391.
About the god
This pendant bearing Serapis's likeness would have been worn by a member of elite Egyptian society.
Walters Art Museum
,
Baltimore
.
"Serapis" is the only form used in Latin, but both
Ancient Greek
:
Σάραπις
Sárapis
and
Ancient Greek
:
Σέραπις
Sérapis
appear in Greek, as well as
Ancient Greek
:
Σαραπo
Serapo
in Bactrian.
His most renowned temple was the
Serapeum of Alexandria
. Under
Ptolemy Soter
, efforts were made to integrate Egyptian religion with that of their Hellenic rulers. Ptolemy's policy was to find a deity that should win the reverence alike of both groups, despite the curses of the Egyptian priests against the gods of the previous foreign rulers (e.g.
Set
, who was lauded by the
Hyksos
).
Alexander the Great
had attempted to use
Amun
for this purpose, but he was more prominent in
Upper Egypt
, and not as popular with those in
Lower Egypt
, where the Greeks had stronger influence. The Greeks had little respect for animal-headed figures, and so a Greek-style
anthropomorphic
statue was chosen as the
idol
, and proclaimed as the equivalent of the highly popular
Apis
. It was named
Aser-hapi
(i.e.
Osiris-Apis
), which became
Serapis
, and was said to be
Osiris
in full, rather than just his
Ka
(life force).
History
The earliest mention of a Serapis is in the disputed death scene of Alexander (323 BC). Here, Serapis has a temple at
Babylon
, and is of such importance that he alone is named as being consulted on behalf of the dying king. His presence in Babylon would radically alter perceptions of the mythologies of this era: the unconnected Babylonian god Ea (
Enki
) was titled
Serapsi
, meaning 'king of the deep', and it is possible this Serapis is the one referred to in the diaries. The significance of this Serapsi in the Hellenic psyche, due to its involvement in Alexander's death, may have also contributed to the choice of Osiris-Apis as the chief Ptolemaic god.
According to
Plutarch
, Ptolemy stole the
cult statue
from
Sinope
, having been instructed in a dream by the "
unknown god
" to bring the statue to
Alexandria
, where the statue was pronounced to be Serapis by two religious experts. One of the experts was of the
Eumolpidae
, the ancient family from whose members the
hierophant
of the
Eleusinian Mysteries
had been chosen since before history, and the other was the scholarly Egyptian priest
Manetho
, which gave weight to the judgement both for the
Egyptians
and the Greeks.
Plutarch may not be correct, however, as some Egyptologists allege that the Sinope in the tale is really the hill of Sinopeion, a name given to the site of the already existing
Serapeum
at
Memphis
. Also, according to
Tacitus
, Serapis (i.e., Apis explicitly identified as Osiris in full) had been the god of the village of
Rhakotis
before it expanded into the great capital of Alexandria.
High Clerk in the Cult of Serapis,
Altes Museum
,
Berlin
The statue suitably depicted a figure resembling
Hades
or
Pluto
, both being kings of the Greek
underworld
, and was shown enthroned with the
modius
, a basket/grain-measure, on his head, since it was a Greek
symbol
for the land of the dead. He also held a
sceptre
in his hand indicating his rulership, with
Cerberus
, gatekeeper of the underworld, resting at his feet, and it also had what appeared to be a
serpent
at its base, fitting the Egyptian symbol of rulership, the
uraeus
.
With his (i.e. Osiris's) wife
Isis
, and their son
Horus
(in the form of
Harpocrates
), Serapis won an important place in the
Greek world
. In his
Description of Greece
, Pausanias notes two
Serapeia
on the slopes of
Acrocorinth
, above the rebuilt Roman city of
Corinth
and one at Copae in Boeotia.
Serapis was among the
international deities
whose cult was received and disseminated throughout the Roman Empire, with
Anubis
sometimes identified with Cerberus. At Rome, Serapis was worshiped in the Iseum Campense, the sanctuary of Isis built during the
Second Triumvirate
in the
Campus Martius
. The Roman cults of Isis and Serapis gained in popularity late in the 1st century when
Vespasian
experienced events he attributed to their miraculous agency while he was in Alexandria, where he stayed before returning to Rome as emperor in 70. From the
Flavian Dynasty
on, Serapis was one of the deities who might appear on imperial coinage with the reigning emperor.
The main cult at Alexandria survived until the late 4th century, when a
Christian mob destroyed the Serapeum of Alexandria
in 385, and the cult was part of the general proscription of religions other than approved forms of Christianity under the
Theodosian decree
.
Gallery
Oil lamp with a bust of Serapis, flanked by a crescent moon and star (Roman-era
Ephesus
, 100-150)
Statuette possibly of Serapis (but note the
herculean
club) from
Begram
,
Afghanistan
Head of Serapis, from a 12-foot statue found off the coast of Alexandria
Head of Serapis (Roman-era Hellenistic terracotta, Staatliches Museum Ägyptischer Kunst, Munich)
Nicopolis ad Istrum
was a
Roman
and Early
Byzantine
town founded by Emperor
Trajan
around 101–106, at the junction of the Iatrus (
Yantra
) and the
Rositsa
rivers, in memory of his victory over the
Dacians
. Its ruins are located at the village of
Nikyup
, 20 km north of
Veliko Tarnovo
in northern
Bulgaria
. The town reached its apogee during the reigns of Trajan,
Hadrian
, the
Antonines
and the
Severan dynasty
.
The classical town was planned according to the orthogonal system. The network of streets, the forum surrounded by an Ionic colonnade and many buildings, a two-nave room later turned into a basilica and other public buildings have been uncovered. The rich architectures and sculptures show a similarity with those of the ancient towns in Asia Minor. Nicopolis ad Istrum had issued coins, bearing images of its own public buildings.
In
447 AD
, the town was destroyed by
Attila's
Huns
. Perhaps it was already abandoned before the early 400s. In the 6th century, it was rebuilt as a powerful fortress enclosing little more than military buildings and churches, following a very common trend for the cities of that century in the Danube area.The largest area of the extensive ruins (21.55 hectares) of the classical Nicopolis was not reoccupied since the fort covered only one fourth of it (5.75 hectares), in the southeastern corner. The town became an episcopal centre during the early Byzantine period. It was finally destroyed by the Avar invasions at the end of the 6th century. A Bulgarian medieval settlement arose upon its ruins later (10th-14th century).
Nicopolis ad Istrum can be said to have been the birthplace of
Germanic
literary tradition. In the 4th century, the
Gothic
bishop, missionary and translator
Ulfilas
(Wulfila) obtained permission from Emperor
Constantius II
to immigrate with his flock of converts to Moesia and settle near Nicopolis ad Istrum in 347-8. There, he invented the
Gothic alphabet
and translated the
Bible
from
Greek
to
Gothic
.
Caracalla 198-217 A.D.
Caesar: 195-198 A.D. (under
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">
Septimius Severus
)
Augustus: 198-217 A.D. (198-209 A.D. with
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">
Septimius Severus
) (209-211 A.D. with
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">
Septimius Severus
and
Geta
) (211 A.D. with
Geta
) (211-217 A.D. Sole Reign)
Son of
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">
Septimius Severus
and
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">
Julia Domna
| Brother of
Geta
| Husband of
<="" font="" color="#000000">
Plautilla
="">
| Nephew of
<="" font="" color="#000000">
Julia Maesa
="">
| Cousin of
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">
Julia Soaemias
and
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">
Julia Mamaea
|
Caracalla
(
Latin
:
Marcus Aurelius Severus Antoninus Augustus
;4 April 188 – 8 April 217) was
Roman emperor
from 198 to 217 The eldest son of
Septimius Severus
, for a short time he ruled jointly with his younger brother
Geta
until he had him murdered in 211. Caracalla is remembered as one of the most notorious and unpleasant of emperors because of the massacres and persecutions he authorized and instigated throughout the Empire.
Caracalla's reign was also notable for the
Constitutio Antoniniana
(also called the Edict of Caracalla), granting
Roman citizenship
to all freemen throughout the
Roman Empire
, which according to historian
Cassius Dio
, was done for the purposes of raising tax revenue. He is also one of the emperors who commissioned a large public bath-house (
thermae
) in Rome. The remains of the
Baths of Caracalla
are still one of the major tourist attractions of the Italian capital.
Early life
Caracalla, of mixed
Punic
–
Roman
and
Syrian
descent, was born Lucius Septimius Bassianus in
Lugdunum
,
Gaul
(now
Lyon
,
France
), the son of the later Emperor Septimius Severus and
Julia Domna
. At the age of seven, his name was changed to Marcus Aurelius Septimius Bassianus Antoninus to create a connection to the family of the philosopher emperor
Marcus Aurelius
. He was later given the
Caracalla
nickname
, which referred to the Gallic hooded tunic he habitually wore and which he made fashionable.
Reign (211)
Murder of brother (211)
His father died in 211 at
Eboracum
(now
York
) while on campaign in northern Britain. Caracalla was present and was then proclaimed emperor by the troops along with his brother
Publius Septimius Antoninus Geta
. Caracalla suspended the
campaign in Caledonia
and soon ended all military activity, as both brothers wanted to be sole ruler thus making relations between them increasingly hostile. When they tried to rule the Empire jointly they actually considered dividing it in halves, but were persuaded not to do so by their mother.
Then in December 211 at a reconciliation meeting arranged by their mother Julia, Caracalla had Geta assassinated by members of the Praetorian Guard loyal to himself, Geta dying in his mother's arms. Caracalla then persecuted and executed most of Geta's supporters and ordered a
damnatio memoriae
pronounced by the Senate against his brother's memory.
Geta's image was simply removed from all coinage, paintings and statues, leaving a blank space next to Caracalla's. Among those executed were his former cousin-wife
Fulvia Plautilla
, his unnamed daughter with Plautilla along with her brother and other members of the family of his former father-in-law
Gaius Fulvius Plautianus
. Plautianus had already been executed for alleged treachery against emperor Severus in 205.
About the time of his accession he ordered the
Roman currency
devalued, the silver purity of the
denarius
was decreased from 56.5% to 51.5%, the actual silver weight dropping from 1.81 grams to 1.66 grams – though the overall weight slightly increased. In 215 he introduced the
antoninianus
, a "double denarius" weighing 5.1 grams and containing 2.6 grams of silver – a purity of 52%.
In the Roman provinces
In 213, Caracalla went north to the German frontier to deal with the
Alamanni
tribesmen who were raiding in the
Agri Decumates
. The Romans did defeat the Alamanni in battle near the river
Main
, but failed to win a decisive victory over them. After a peace agreement was brokered and a large bribe payment given to the invaders, the Senate conferred upon him the empty title of
Germanicus Maximus
. He also acquired the surname
Alemannicus
at this time. The following year the tyrant traveled to the East, to Syria and Egypt never to return to Rome.
Gibbon
in his work describes Caracalla as "the common enemy of mankind". He left the capital in 213, about a year after the murder of Geta, and spent the rest of his reign in the provinces, particularly those of the East. He kept the Senate and other wealthy families in check by forcing them to construct, at their own expense, palaces, theaters, and places of entertainment throughout the periphery. New and heavy taxes were levied against the bulk of the population, with additional fees and confiscations targeted at the wealthiest families.
When the inhabitants of
Alexandria
heard Caracalla's claims that he had killed Geta in self-defense, they produced a satire mocking this as well as Caracalla's other pretensions. In 215, Caracalla savagely responded to this insult by slaughtering the deputation of leading citizens who had unsuspectingly assembled before the city to greet his arrival, and then unleashed his troops for several days of looting and plunder in Alexandria. According to historian Cassius Dio, over 20,000 people were killed.
[
citation needed
]
Domestic Roman policy
Affiliation with the army
During his reign as emperor, Caracalla raised the annual pay of an average legionary to 675
denarii
and lavished many benefits on the army which he both feared and admired, as instructed by his father Septimius Severus who had told him on his deathbed to always mind the soldiers and ignore everyone else. Caracalla did manage to win the trust of the military with generous pay rises and popular gestures, like marching on foot among the ordinary soldiers, eating the same food, and even grinding his own flour with them.
With the soldiers, "He forgot even the proper dignity of his rank, encouraging their insolent familiarity," according to Gibbon. "The vigour of the army, instead of being confirmed by the severe discipline of the camps, melted away in the luxury of the cities."
His official portraiture marks a break with the detached images of the philosopher–emperors who preceded him: his close-cropped haircut is that of a soldier, his pugnacious scowl a realistic and threatening presence. This rugged soldier–emperor iconic archetype was adopted by most of the following emperors who depended on the support of the troops to rule, like his eventual successor
Maximinus Thrax
.
Seeking to secure his own legacy, Caracalla also commissioned one of Rome's last major architectural achievements, the
Baths of Caracalla
, the 2nd largest public baths ever built in ancient Rome. The main room of the baths was larger than
St. Peter's Basilica
, and could easily accommodate over 2,000 Roman citizens at one time. The bath house opened in 216, complete with libraries, private rooms and outdoor tracks. Internally it was lavishly decorated with gold-trimmed marble floors, columns, mosaics and colossal statuary.
Edict of Caracalla (212)
The
Constitutio Antoniniana
(Latin: "Constitution [or Edict] of Antoninus") (also called
Edict of Caracalla
) was an edict issued in 212 by Caracalla which declared that all free men in the Roman Empire were to be given full Roman citizenship and all free women in the Empire were given the same rights as Roman women.
Before 212, for the most part only inhabitants of Italia held full Roman citizenship. Colonies of Romans established in other provinces, Romans (or their descendants) living in provinces, the inhabitants of various cities throughout the Empire, and small numbers of local nobles (such as kings of client countries) held full citizenship also. Provincials, on the other hand, were usually non-citizens, although many held the
Latin Right
.
The Roman Historian
Cassius Dio
contended that the sole motivation for the edict was a desire to increase state revenue.At the time aliens did not have to pay most taxes that were required of citizens, so although nominally Caracalla was elevating their legal status, he was more importantly expanding the Roman tax base. The effect of this was to remove the distinction that citizenship had held since the foundation of Rome and as such the act had a profound effect upon the fabric of Roman society.
War with Parthia
According to the historian Herodian, in 216, Caracalla tricked the Parthians into believing that he accepted a marriage and peace proposal, but then had the bride and guests slaughtered after the wedding celebrations. The thereafter ongoing conflict and skirmishes became known as the
Parthian war of Caracalla
.
Assassination (217)
The Roman Empire during the reign of Caracalla.
While travelling from
Edessa
to continue the war with
Parthia
, he was assassinated while urinating at a roadside near
Carrhae
on 8 April 217 (4 days after his 29th birthday), by Julius Martialis, an officer of his personal bodyguard.
Herodian
says that Martialis' brother had been executed a few days earlier by Caracalla on an unproven charge; Cassius Dio, on the other hand, says that Martialis was resentful at not being promoted to the rank of centurion. The escort of the emperor gave him privacy to relieve himself, and Martialis then ran forward and killed Caracalla with a single sword stroke. While attempting to flee, the bold assassin was then quickly dispatched by a Scythian archer of the Imperial Guard.
Caracalla was succeeded by his
Praetorian Guard Prefect
,
Macrinus
, who (according to Herodian) was most probably responsible for having the emperor assassinated.
His nickname
According to
Aurelius Victor
in his
Epitome de Caesaribus
, the
agnomen
"Caracalla" refers to a Gallic
cloak
that Caracalla adopted as a personal fashion, which spread to his army and his court. Cassius Dio and the
Historia Augusta
agree that his nickname was derived from his cloak, but do not mention its country of origin.
Legendary king of Britain
Geoffrey of Monmouth
's legendary
History of the Kings of Britain
makes Caracalla a king of Britain, referring to him by his actual name "Bassianus", rather than the nickname Caracalla. In the story, after Severus's death the Romans wanted to make Geta king of Britain, but the Britons preferred Bassianus because he had a British mother. The two brothers fought a battle in which Geta was killed and Bassianus succeeded to the throne. He ruled until he was betrayed by his
Pictish
allies and overthrown by
Carausius
, who, according to Geoffrey, was a Briton, rather than the historically much later
Menapian
Gaul that he actually was.
="">="">="">="">="">="">="">="">
Frequently Asked Questions
How long until my order is shipped?
Depending on the volume of sales, it may take up to 5 business days for shipment of your order after the receipt of payment.
How will I know when the order was shipped?
After your order has shipped, you will be left positive feedback, and that date should be used as a basis of estimating an arrival date.
After you shipped the order, how long will the mail take?
USPS First Class mail takes about 3-5 business days to arrive in the U.S., international shipping times cannot be estimated as they vary from country to country. I am not responsible for any USPS delivery delays, especially for an international package.
What is a certificate of authenticity and what guarantees do you give that the item is authentic?
Each of the items sold here, is provided with a Certificate of Authenticity, and a Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity, issued by a world-renowned numismatic and antique expert that has identified over 10000 ancient coins and has provided them with the same guarantee. You will be quite happy with what you get with the COA; a professional presentation of the coin, with all of the relevant information and a picture of the coin you saw in the listing.
Compared to other certification companies, the certificate of authenticity is a -50 value. So buy a coin today and own a piece of history, guaranteed.
Is there a money back guarantee?
I offer a 30 day unconditional money back guarantee. I stand behind my coins and would be willing to exchange your order for either store credit towards other coins, or refund, minus shipping expenses, within 30 days from the receipt of your order. My goal is to have the returning customers for a lifetime, and I am so sure in my coins, their authenticity, numismatic value and beauty, I can offer such a guarantee.
Is there a number I can call you with questions about my order?
You can contact me directly via ask seller a question and request my telephone number, or go to my About Me Page to get my contact information only in regards to items purchased on eBay.
When should I leave feedback?
Once you receive your order, please leave a positive. Please don't leave any negative feedbacks, as it happens many times that people rush to leave feedback before letting sufficient time for the order to arrive. Also, if you sent an email, make sure to check for my reply in your messages before claiming that you didn't receive a response. The matter of fact is that any issues can be resolved, as reputation is most important to me. My goal is to provide superior products and quality of service.