-40%
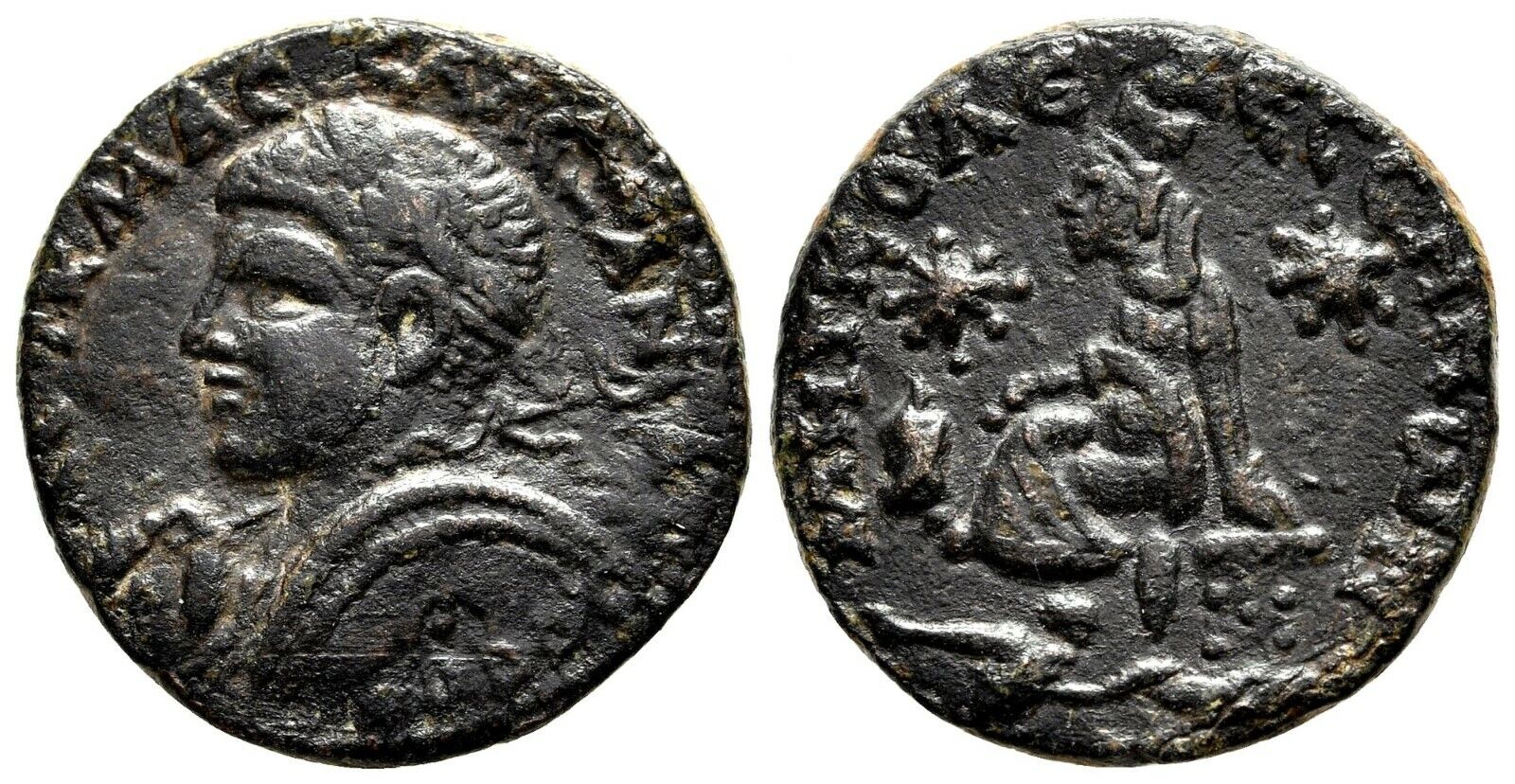
CARACALLA 198AD Pautalia Thrace TEMPLE of HYGEIA Medicine Roman Coin RARE i58088
$ 47.52
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
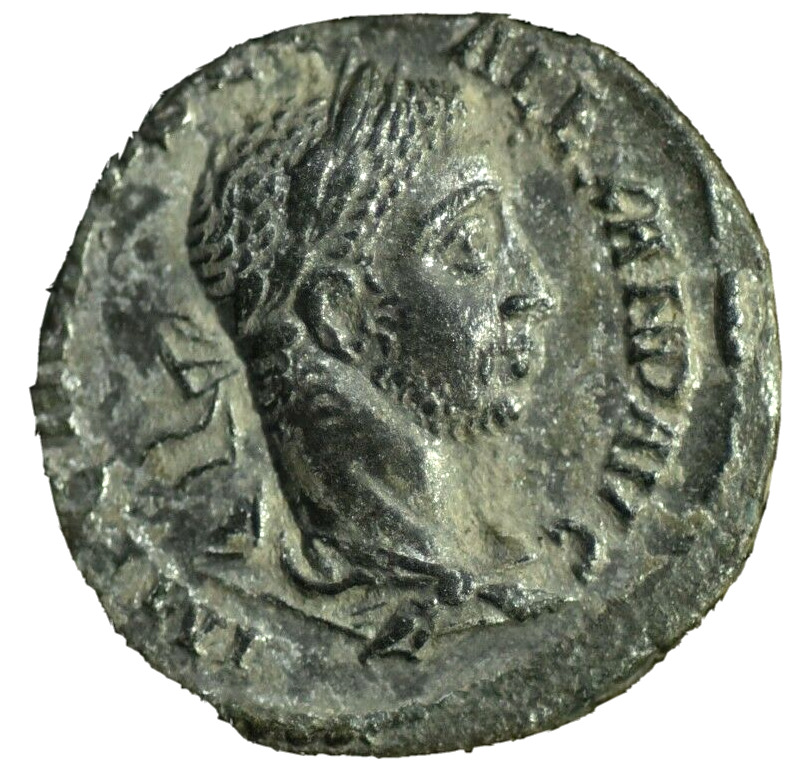
Item:i58088
Authentic Ancient Coin of:
Caracalla - Roman Emperor: 198-217 A.D.
Bronze 28mm (15.38 grams) of Pautalia in Thrace
Laureate head right.
OVΛΠIAC ΠAVTAΛIAC, Tetrastyle (four-column) temple with statue of Hygeia within standing holding serpent which she feeds from patera.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
In
Greek
and
Roman mythology
,
Hygieia
(also
Hygiea
or
Hygeia
, Greek
Ὑγιεία
or
Ὑγεία
, Latin
Hygēa
or
Hygīa
), was the daughter of the god of medicine,
Asclepius
, and
Epione
. She was the goddess/personification of health, cleanliness and sanitation.
Hygieia and her five sisters each performed a facet of
Apollo
's art: Hygieia ("Hygiene" the goddess/personification of health, cleanliness, and sanitation),
Panacea
(the goddess of Universal remedy),
Iaso
(the goddess of recuperation from illness),
Aceso
(the goddess of the healing process).
Hygieia also played an important part in her father's
cult
. While her father was more directly associated with healing, she was associated with the prevention of sickness and the continuation of good health. Her name is the source of the word "
hygiene
". She was imported by the Romans as the Goddess Valetudo, the goddess of personal health, but in time she started to be increasingly identified with the ancient Italian goddess of social welfare,
Salus
.
History
At Athens, Hygieia was the subject of a local cult since at least the 7th century BC. "Athena Hygieia" was one of the cult titles given to
Athena
, as Plutarch recounts of the building of the
Parthenon
(447-432 BC):
“
A strange accident happened in the course of building, which showed that the goddess was not averse to the work, but was aiding and co-operating to bring it to perfection. One of the artificers, the quickest and the handiest workman among them all, with a slip of his foot fell down from a great height, and lay in a miserable condition, the physicians having no hope of his recovery. When Pericles was in distress about this, the goddess [Athena] appeared to him at night in a dream, and ordered a course of treatment, which he applied, and in a short time and with great ease cured the man. And upon this occasion it was that he set up a brass statue of Athena Hygieia, in the citadel near the altar, which they say was there before. But it was
Phidias
who wrought the goddess's image in gold, and he has his name inscribed on the pedestal as the workman of it.
”
However, the cult of Hygieia as an independent goddess did not begin to spread out until the
Delphic oracle
recognized her, and after the devastating
Plague of Athens
(430-427 BC) and in Rome in 293 BC.
In the 2nd century AD,
Pausanias
noted the statues both of Hygieia and of Athena Hygieia near the entrance to the
Acropolis
of Athens.
Worship
Hygieia's primary temples were in
Epidaurus
,
Corinth
,
Cos
and
Pergamon
.
Pausanias
remarked that, at the
Asclepieion
of
Titane
in
Sicyon
(founded by
Alexanor
, Asclepius' grandson), statues of Hygieia were covered by women's hair and pieces of
Babylonian
clothes. According to inscriptions, the same sacrifices were offered at
Paros
.
Ariphron
, a Sicyonian artist from the 4th century BC wrote a well-known
hymn
celebrating her. Statues of Hygieia were created by
Scopas
,
Bryaxis
and
Timotheus
, among others, but there is no clear description of what they looked like. She was often depicted as a young woman feeding a large snake that was wrapped around her body or drinking from a jar that she carried. These attributes were later adopted by the
Gallo-Roman
healing goddess,
Sirona
. Hygieia was accompanied by her brother,
Telesphorus
.
The
Pythagoreans
called the pentagram ὑγιεία
Hugieia
("health"); also the Greek goddess of health,
Hygieia
and saw in the pentagram a mathematical perfection.
Kyustendil
(
Bulgarian
:
Кюстендил
, historically
Велбъжд
,
Velbazhd
) is a town in the far west of
Bulgaria
, the capital of
Kyustendil Province
, with a population of 58,059 (2005 census). Kyustendil is situated in the southern part of the Kyustendil Valley, 90 km southwest of
Sofia
. It was named after the medieval lord of the surrounding region,
Constantine Dragaš
.
A
Thracian
settlement was founded at the place of the modern town in the
5th
-4th century BC and the
Romans
developed it into an important stronghold, balneological resort and trade junction called
Pautalia
in the 1st century AD.
The
Hisarlaka
fortress was built in the 4th century and the town was mentioned under the
Slavic
name of
Velbazhd
(Велбъжд, meaning "camel") in a 1019 charter by the
Byzantine
Emperor
Basil II
. It became a major religious and administrative centre.
Caracalla 198-217 A.D.
Caesar: 195-198 A.D. (under
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">Septimius Severus="">
)
Augustus: 198-217 A.D. (198-209 A.D. with
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">Septimius Severus) (209-211 A.D. with
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">Septimius Severus and
Geta
) (211 A.D. with
Geta
) (211-217 A.D. Sole Reign)
Son of
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">Septimius Severus and
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">Julia Domna | Brother of
Geta
| Husband of
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">Plautilla
| Nephew of
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">Julia Maesa | Cousin of
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">Julia Soaemias and
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">Julia Mamaea |
Caracalla
(
Latin
:
Marcus Aurelius Severus Antoninus Augustus
;4 April 188 – 8 April 217) was
Roman emperor
from 198 to 217 The eldest son of
Septimius Severus
, for a short time he ruled jointly with his younger brother
Geta
until he had him murdered in 211. Caracalla is remembered as one of the most notorious and unpleasant of emperors because of the massacres and persecutions he authorized and instigated throughout the Empire.
Caracalla's reign was also notable for the
Constitutio Antoniniana
(also called the Edict of Caracalla), granting
Roman citizenship
to all freemen throughout the
Roman Empire
, which according to historian
Cassius Dio
, was done for the purposes of raising tax revenue. He is also one of the emperors who commissioned a large public bath-house (
thermae
) in Rome. The remains of the
Baths of Caracalla
are still one of the major tourist attractions of the Italian capital.
Early life
Caracalla, of mixed
Punic
,
Roman
and
Syrian
descent, was born Lucius Septimius Bassianus in
Lugdunum
,
Gaul
(now
Lyon
,
France
), the son of the later Emperor Septimius Severus and
Julia Domna
. At the age of seven, his name was changed to Marcus Aurelius Septimius Bassianus Antoninus to create a connection to the family of the philosopher emperor
Marcus Aurelius
. He was later given the
Caracalla
nickname
, which referred to the Gallic hooded tunic he habitually wore and which he made fashionable.
Reign (211)
Murder of brother (211)
His father died in 211 at
Eboracum
(now
York
) while on campaign in northern Britain. Caracalla was present and was then proclaimed emperor by the troops along with his brother
Publius Septimius Antoninus Geta
. Caracalla suspended the
campaign in Caledonia
and soon ended all military activity, as both brothers wanted to be sole ruler thus making relations between them increasingly hostile. When they tried to rule the Empire jointly they actually considered dividing it in halves, but were persuaded not to do so by their mother.
Then in December 211 at a reconciliation meeting arranged by their mother Julia, Caracalla had Geta assassinated by members of the Praetorian Guard loyal to himself, Geta dying in his mother's arms. Caracalla then persecuted and executed most of Geta's supporters and ordered a
damnatio memoriae
pronounced by the Senate against his brother's memory.
Geta's image was simply removed from all coinage, paintings and statues, leaving a blank space next to Caracalla's. Among those executed were his former cousin-wife
Fulvia Plautilla
, his unnamed daughter with Plautilla along with her brother and other members of the family of his former father-in-law
Gaius Fulvius Plautianus
. Plautianus had already been executed for alleged treachery against emperor Severus in 205.
About the time of his accession he ordered the
Roman currency
devalued, the silver purity of the
denarius
was decreased from 56.5% to 51.5%, the actual silver weight dropping from 1.81 grams to 1.66 grams – though the overall weight slightly increased. In 215 he introduced the
antoninianus
, a "double denarius" weighing 5.1 grams and containing 2.6 grams of silver – a purity of 52%.
In the Roman provinces
In 213, Caracalla went north to the German frontier to deal with the
Alamanni
tribesmen who were raiding in the
Agri Decumates
. The Romans did defeat the Alamanni in battle near the river
Main
, but failed to win a decisive victory over them. After a peace agreement was brokered and a large bribe payment given to the invaders, the Senate conferred upon him the empty title of
Germanicus Maximus
. He also acquired the surname
Alemannicus
at this time. The following year the tyrant traveled to the East, to Syria and Egypt never to return to Rome.
Gibbon
in his work describes Caracalla as "the common enemy of mankind". He left the capital in 213, about a year after the murder of Geta, and spent the rest of his reign in the provinces, particularly those of the East. He kept the Senate and other wealthy families in check by forcing them to construct, at their own expense, palaces, theaters, and places of entertainment throughout the periphery. New and heavy taxes were levied against the bulk of the population, with additional fees and confiscations targeted at the wealthiest families.
When the inhabitants of
Alexandria
heard Caracalla's claims that he had killed Geta in self-defense, they produced a satire mocking this as well as Caracalla's other pretensions. In 215, Caracalla savagely responded to this insult by slaughtering the deputation of leading citizens who had unsuspectingly assembled before the city to greet his arrival, and then unleashed his troops for several days of looting and plunder in Alexandria. According to historian Cassius Dio, over 20,000 people were killed.
[
Domestic Roman policy
Affiliation with the army
During his reign as emperor, Caracalla raised the annual pay of an average legionary to 675
denarii
and lavished many benefits on the army which he both feared and admired, as instructed by his father Septimius Severus who had told him on his deathbed to always mind the soldiers and ignore everyone else. Caracalla did manage to win the trust of the military with generous pay rises and popular gestures, like marching on foot among the ordinary soldiers, eating the same food, and even grinding his own flour with them.
With the soldiers, "He forgot even the proper dignity of his rank, encouraging their insolent familiarity," according to Gibbon. "The vigour of the army, instead of being confirmed by the severe discipline of the camps, melted away in the luxury of the cities."
His official portraiture marks a break with the detached images of the philosopher–emperors who preceded him: his close-cropped haircut is that of a soldier, his pugnacious scowl a realistic and threatening presence. This rugged soldier–emperor iconic archetype was adopted by most of the following emperors who depended on the support of the troops to rule, like his eventual successor
Maximinus Thrax
.
Seeking to secure his own legacy, Caracalla also commissioned one of Rome's last major architectural achievements, the
Baths of Caracalla
, the 2nd largest public baths ever built in ancient Rome. The main room of the baths was larger than
St. Peter's Basilica
, and could easily accommodate over 2,000 Roman citizens at one time. The bath house opened in 216, complete with libraries, private rooms and outdoor tracks. Internally it was lavishly decorated with gold-trimmed marble floors, columns, mosaics and colossal statuary.
Edict of Caracalla (212)
The
Constitutio Antoniniana
(Latin: "Constitution [or Edict] of Antoninus") (also called
Edict of Caracalla
) was an edict issued in 212 by Caracalla which declared that all free men in the Roman Empire were to be given full Roman citizenship and all free women in the Empire were given the same rights as Roman women.
Before 212, for the most part only inhabitants of Italia held full Roman citizenship. Colonies of Romans established in other provinces, Romans (or their descendants) living in provinces, the inhabitants of various cities throughout the Empire, and small numbers of local nobles (such as kings of client countries) held full citizenship also. Provincials, on the other hand, were usually non-citizens, although many held the
Latin Right
.
The Roman Historian
Cassius Dio
contended that the sole motivation for the edict was a desire to increase state revenue.At the time aliens did not have to pay most taxes that were required of citizens, so although nominally Caracalla was elevating their legal status, he was more importantly expanding the Roman tax base. The effect of this was to remove the distinction that citizenship had held since the foundation of Rome and as such the act had a profound effect upon the fabric of Roman society.
War with Parthia
According to the historian Herodian, in 216, Caracalla tricked the Parthians into believing that he accepted a marriage and peace proposal, but then had the bride and guests slaughtered after the wedding celebrations. The thereafter ongoing conflict and skirmishes became known as the
Parthian war of Caracalla
.
Assassination (217)
The Roman Empire during the reign of Caracalla.
While travelling from
Edessa
to continue the war with
Parthia
, he was assassinated while urinating at a roadside near
Carrhae
on 8 April 217 (4 days after his 29th birthday), by Julius Martialis, an officer of his personal bodyguard.
Herodian
says that Martialis' brother had been executed a few days earlier by Caracalla on an unproven charge; Cassius Dio, on the other hand, says that Martialis was resentful at not being promoted to the rank of centurion. The escort of the emperor gave him privacy to relieve himself, and Martialis then ran forward and killed Caracalla with a single sword stroke. While attempting to flee, the bold assassin was then quickly dispatched by a Scythian archer of the Imperial Guard.
Caracalla was succeeded by his
Praetorian Guard Prefect
,
Macrinus
, who (according to Herodian) was most probably responsible for having the emperor assassinated.
His nickname
According to
Aurelius Victor
in his
Epitome de Caesaribus
, the
agnomen
"Caracalla" refers to a Gallic
cloak
that Caracalla adopted as a personal fashion, which spread to his army and his court. Cassius Dio and the
Historia Augusta
agree that his nickname was derived from his cloak, but do not mention its country of origin.
Legendary king of Britain
Geoffrey of Monmouth
's legendary
History of the Kings of Britain
makes Caracalla a king of Britain, referring to him by his actual name "Bassianus", rather than the nickname Caracalla. In the story, after Severus's death the Romans wanted to make Geta king of Britain, but the Britons preferred Bassianus because he had a British mother. The two brothers fought a battle in which Geta was killed and Bassianus succeeded to the throne. He ruled until he was betrayed by his
Pictish
allies and overthrown by
Carausius
, who, according to Geoffrey, was a Briton, rather than the historically much later
Menapian
Gaul that he actually was.
Frequently Asked Questions
Mr. Ilya Zlobin, world-renowned expert numismatist, enthusiast, author and dealer in authentic ancient Greek, ancient Roman, ancient Byzantine, world coins & more.
Who am I dealing with?
You are dealing with Ilya Zlobin, ancient coin expert, enthusiast, author and dealer with an online store having a selection of over 15,000 items with great positive feedback from verified buyers and over 10 years experience dealing with over 57,000 ancient and world coins and artifacts. Ilya Zlobin is an independent individual who has a passion for coin collecting, research and understanding the importance of the historical context and significance all coins and objects represent. Most others are only concerned with selling you, Ilya Zlobin is most interested in educating you on the subject, and providing the largest selection, most professional presentation and service for the best long-term value for collectors worldwide creating returning patrons sharing in the passion of ancient and world coin collecting for a lifetime.
How long until my order is shipped?
Orders are shipped by the next business day (after receipt of payment) most of the time.
How will I know when the order was shipped?
After your order has shipped, you will be left positive feedback, and that date could be used as a basis of estimating an arrival date. Any tracking number would be found under your 'Purchase history' tab.
USPS First Class mail takes about 3-5 business days to arrive in the U.S. International shipping times cannot be estimated as they vary from country to country.
Standard international mail to many countries
does not
include a tracking number, and can also be slow sometimes.
For a tracking number and signature confirmation, you may want to do Express Mail International Shipping, which costs more, however, is the fastest and most secure. Additionally you may be able to receive your order in as little as 3-5 business days using this method. For Express Mail International, it may be possible to place up to 10-15 items in one package (for the one shipping cost) as it is flat rate envelope, which may be the most cost-effective, secure and fastest way to receive items internationally. Send me a message about this and I can update your invoice should you want this method.
Getting your order to you, quickly and securely is a top priority and is taken seriously here.
Great care is taken in packaging and mailing every item securely and quickly.
Please be aware, I cannot take responsibility for any postal service delivery delays, especially for international packages as it may happen in rare instances.
What is a certificate of authenticity and what guarantees do you give that the item is authentic?
Each of the items sold here, is provided with a Certificate of Authenticity, and a Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity, issued by a world-renowned numismatic and antique expert that has identified over 57,000 ancient coins and has provided them with the same guarantee. You will be very happy with what you get with the COA; a professional presentation of the coin, with all of the relevant information and a picture of the coin you saw in the listing. Additionally, the coin is inside it's own protective coin flip (holder), with a 2x2 inch description of the coin matching the individual number on the COA.
On the free-market such a presentation alone, can be considered a - value all in itself, and it comes standard with your purchases from me,
FREE.
With every purchase, you are leveraging my many years of experience to get a more complete context and understanding of the piece of history you are getting. Whether your goal is to collect or give the item as a gift, coins presented like this could be more prized and valued higher than items that were not given such care and attention to.
Buy a coin today and own a piece of history, guaranteed.
Is there a money back guarantee?
I offer a 30 day unconditional money back guarantee. I stand behind my coins and would be willing to exchange your order for either store credit towards other coins, or refund, minus shipping expenses, within 30 days from the receipt of your order. My goal is to have the returning customers for a lifetime, and I am so sure in my coins, their authenticity, numismatic value and beauty, I can offer such a guarantee.
Is there a number I can call you with questions about my order?
You can contact me directly via ask seller a question and request my telephone number, or go to my About Me Page to get my contact information only in regards to items purchased on eBay.
When should I leave feedback?
Once you receive your order, please leave a positive feedback. Please don't leave any negative feedbacks, as it happens sometimes that people rush to leave feedback before letting sufficient time for their order to arrive. Also, if you sent an email, make sure to check for my reply in your messages before claiming that you didn't receive a response. The matter of fact is that any issues can be resolved, as reputation is most important to me. My goal is to provide superior products and quality of service.
How and where do I learn more about collecting ancient coins?
Visit the "Guide on How to Use My Store" for on an overview about using my store, with additional information and links to all other parts of my store which may include educational information on topics you are looking for.
You may also want to do a YouTube search for the term "ancient coin collecting" for educational videos on this topic.
="">="">="">="">="">="">="">="">